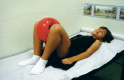
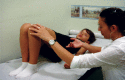
Comparative, prospective, and randomized study between urotherapy and the pharmacological treatment of children with urinary incontinence
- PMID: 23843062
- PMCID: PMC4872895
- DOI: 10.1590/s1679-45082013000200012
Comparative, prospective, and randomized study between urotherapy and the pharmacological treatment of children with urinary incontinence
Abstract
Objective: To verify and compare the results of behavioral modification plus pelvic floor muscle training and behavioral modifications plus oxybutynin chloride in children with nonmonosymptomatic enuresis.
Methods: A total of 47 children were randomized using opaque and sealed envelopes sequentially numbered. Group I was composed of 21 children who underwent antimuscarinic treatment (oxybutynin), and Group II was composed of 26 patients who underwent pelvic floor muscle training. Both groups were instructed as to behavioral modifications.
Results: The voiding diary results were compared each month between Groups I and II. In the first month of treatment, children in Group I presented 12.2 dry nights, 13.4 in the second month, and 15.9 in the last month. In Group II, the results were: 14.9 dry nights in the first month, 20.8 dry nights in the second and 24.0 dry nights in the last month. There was a significant difference between the groups in second and third months.
Conclusion: Pelvic floor exercises associated with behavioral changes were more effective than pharmacological treatment in children with urinary incontinence.
Objetivo:: Verificar e comparar os resultados da modificação comportamental associado ao treinamento dos músculos do assoalho pélvico e modificação comportamental associado ao uso de cloridrato de oxibutinina em crianças com enurese não monossintomática.
Métodos:: Foram randomizadas 47 crianças por meio de envelopes opacos e selados com numeração sequencial. O Grupo I foi composto por 21 crianças que receberam tratamento com antimuscarínico (oxibutinina) e o Grupo II por 26 pacientes que receberam treinamento dos músculos do assoalho pélvico. Ambos os grupos foram instruídos em relação à modificação comportamental.
Resultados:: Os resultados do diário miccional foram comparados cada mês entre os Grupos I e II. No primeiro mês de tratamento, as crianças do Grupo I apresentaram 12,2 noites secas, 13,4 no segundo mês e 15,9 no último mês. No Grupo II, os resultados foram: 14,9 noites secas no primeiro mês, 20,8 no segundo mês e 24,0 no último mês. Houve diferença significativa entre os grupos no segundo e no terceiro mês.
Conclusão:: Os exercícios do assoalho pélvico associados a mudança comportamental foram mais efetivos do que o tratamento farmacológico em crianças com incontinência urinária.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pelvic floor muscle training alone or in combination with oxybutynin in treatment of nonmonosymptomatic enuresis. A randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow up.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019 Jun 27;17(3):eAO4602. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2019AO4602. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31271608 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cochrane Review Summary: Pelvic floor muscle training added to another active treatment versus the same active treatment alone for urinary incontinence in women.Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2015 Nov;16(6):545-7. doi: 10.1017/S1463423615000419. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2015. PMID: 26244696 Review. No abstract available.
-
Combined functional pelvic floor muscle exercises with Swiss ball and urotherapy for management of dysfunctional voiding in children: a randomized clinical trial.Eur J Pediatr. 2014 Oct;173(10):1347-53. doi: 10.1007/s00431-014-2336-0. Epub 2014 May 21. Eur J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24844352 Clinical Trial.
-
Multi-center randomized controlled trial of cognitive treatment, placebo, oxybutynin, bladder training, and pelvic floor training in children with functional urinary incontinence.Neurourol Urodyn. 2014 Jun;33(5):482-7. doi: 10.1002/nau.22446. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014. PMID: 23775924 Clinical Trial.
-
[Pelvic floor rehabilitation for female urinary incontinence: mechanisms of action].Prog Urol. 2013 Jun;23(8):491-501. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 May 2. Prog Urol. 2013. PMID: 23725579 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Conservative interventions for treating functional daytime urinary incontinence in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 18;9(9):CD012367. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012367.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31532563 Free PMC article.
-
Pelvic floor muscle training alone or in combination with oxybutynin in treatment of nonmonosymptomatic enuresis. A randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow up.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019 Jun 27;17(3):eAO4602. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2019AO4602. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31271608 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Optimising the management of children with concomitant bladder dysfunction and behavioural disorders.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2023 Oct;32(10):1989-1999. doi: 10.1007/s00787-022-02016-4. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 35767104 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nevéus T, von Gontard A, Hoebeke P, Hjälmås K, Bauer S, Bower W, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: report from the Standardisation Committee of the International Children's Continence Society. J Urol. 2006;176(1):314–324. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann F, Steuber C, Günther J, Glaeske G, Bachmann CJ. Which treatments do children with newly diagnosed non-organic urinary incontinence receive? An analysis of 3,188 outpatient cases from Germany. Neurourology and Urodyn. 2012;31(1):93–98. - PubMed
-
- Shafik A, Shafik IA. Overactive bladder inhibition in response to pelvic floor muscle exercises. World J Urol. 2003;20(6):374–377. - PubMed
-
- Caione P, Arena F, Biraghi M, Cigna RM, Chendi D, Chiozza ML, et al. Nocturnal enuresis and daytime wetting: A multicentric trial with oxybutynin and desmopressin. Eur Urol. 1997;31(4):459–463. - PubMed
-
- Zivkovic V, Lazovic M, Vlajkovic M, Slavkovic A, Dimitrijevic L, Stankovic I, et al. Diaphragmatic breathing exercises and pelvic floor retraining in children with dysfunctional voiding. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;48(3):413–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical