Treatment of strongyloidiasis in HTLV-1 and Strongyloides stercoralis coinfected patients is associated with increased TNFα and decreased soluble IL2 receptor levels
- PMID: 23843560
- PMCID: PMC3735360
- DOI: 10.1093/trstmh/trt052
Treatment of strongyloidiasis in HTLV-1 and Strongyloides stercoralis coinfected patients is associated with increased TNFα and decreased soluble IL2 receptor levels
Abstract
Background: Human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection has been associated with recurrent and disseminated strongyloidiasis and adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL).
Methods: We compared immunological aspects and markers for ATLL in HTLV-1 patients with or without strongyloidiasis, and evaluated the influence of Strongyloides stercoralis treatment on the immune response and clinical outcomes of HTLV-1 infection.
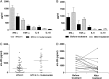
Results: Levels of TNFα and IFNγ were lower in patients coinfected with HTLV-1 and S. stercoralis than in patients with HTLV-1 only (p < 0.05), and there was an increase in TNFα levels after anthelmintic treatment. Levels of sIL-2R were higher in patients with HTLV-1 coinfected with S. stercoralis and anthelmintic treatment decreased sIL-2R levels (p < 0.05). The one patient who developed ATLL was coinfected with S. stercoralis.
Conclusion: These data show that helminthic infection has a modulatory role in HTLV-1 infection and that S. stercoralis may be a cofactor in the development of ATLL.
Keywords: ATLL; HTLV-1; Interleukin-2 receptor; Leukemia; Strongyloides stercoralis; sIL-2R.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Case Report: Strongyloides stercoralis Hyperinfection in a Patient with HTLV-1: An Infection with Filariform and Rhabditiform Larvae, Eggs, and Free-Living Adult Females Output.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018 Dec;99(6):1583-1586. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0402. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018. PMID: 30277207 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal outcome in a patient under immunosuppressant therapy infected with human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1), cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Strongyloides stercoralis: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 2;20(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05195-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32615937 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of host immune response against strongyloides stercoralis by human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006 Feb;74(2):246-9. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006. PMID: 16474078
-
Epidemiological and clinical interaction between HTLV-1 and Strongyloides stercoralis.Parasite Immunol. 2004 Nov-Dec;26(11-12):487-97. doi: 10.1111/j.0141-9838.2004.00726.x. Parasite Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15771684 Review.
-
[Clinical and immunological consequences of the association between HTLV-1 and strongyloidiasis].Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2002 Nov-Dec;35(6):641-9. doi: 10.1590/s0037-86822002000600016. Epub 2003 Feb 26. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2002. PMID: 12612748 Review. Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 and Strongyloides stercoralis Co-infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 14;9:832430. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.832430. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35237633 Free PMC article.
-
Strongyloides stercoralis and HTLV-1 coinfection in CD34+ cord blood stem cell humanized mice: Alteration of cytokine responses and enhancement of larval growth.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jul 27;15(7):e0009559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009559. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34314415 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic profile of immune factors in an elderly Italian population affected by chronic strongyloidiasis.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Oct 15;13(1):515. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04391-w. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 33059754 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphotropic Viruses EBV, KSHV and HTLV in Latin America: Epidemiology and Associated Malignancies. A Literature-Based Study by the RIAL-CYTED.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 4;12(8):2166. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082166. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32759793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strongyloidiasis.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024 Jan 25;10(1):6. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00490-x. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024. PMID: 38272922 Review.
References
-
- Porto AF, Neva FA, Bittencourt H, et al. HTLV-1 decreases Th2 type of immune response in patients with strongyloidiasis. Parasite Immunol. 2001;23:503–7. - PubMed
-
- Gotuzzo E, Terashima A, Alvarez H, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection associated with human T cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection in Peru. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:146–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

