Signaling inputs to invadopodia and podosomes
- PMID: 23843616
- PMCID: PMC3711196
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.079475
Signaling inputs to invadopodia and podosomes
Abstract
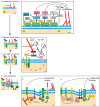
Remodeling of extracellular matrix (ECM) is a fundamental cell property that allows cells to alter their microenvironment and move through tissues. Invadopodia and podosomes are subcellular actin-rich structures that are specialized for matrix degradation and are formed by cancer and normal cells, respectively. Although initial studies focused on defining the core machinery of these two structures, recent studies have identified inputs from both growth factor and adhesion signaling as crucial for invasive activity. This Commentary will outline the current knowledge on the upstream signaling inputs to invadopodia and podosomes and their role in governing distinct stages of these invasive structures. We discuss invadopodia and podosomes as adhesion structures and highlight new data showing that invadopodia-associated adhesion rings promote the maturation of already-formed invadopodia. We present a model in which growth factor stimulation leads to phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activity and formation of invadopodia, whereas adhesion signaling promotes exocytosis of proteinases at invadopodia.
Keywords: Actin cytoskeleton; Adhesion; Growth factor; Invadopodia; PI3K; Podosome; phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Podosome-like structures of non-invasive carcinoma cells are replaced in epithelial-mesenchymal transition by actin comet-embedded invadopodia.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Jun;14(6B):1569-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00868.x. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 19656240 Free PMC article.
-
CRP2, a new invadopodia actin bundling factor critically promotes breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):13688-705. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7327. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26883198 Free PMC article.
-
5'-Inositol phosphatase SHIP2 recruits Mena to stabilize invadopodia for cancer cell invasion.J Cell Biol. 2016 Sep 12;214(6):719-34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201501003. Epub 2016 Sep 5. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27597754 Free PMC article.
-
The matrix corroded: podosomes and invadopodia in extracellular matrix degradation.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;17(3):107-17. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.01.002. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17275303 Review.
-
Biogenesis of invadopodia and their cellular functions.Postepy Biochem. 2014;60(1):62-8. Postepy Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25033543 Review.
Cited by
-
RET isoforms contribute differentially to invasive processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Oncogene. 2020 Oct;39(41):6493-6510. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01448-z. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32884116
-
Cytoplasmic LIF reprograms invasive mode to enhance NPC dissemination through modulating YAP1-FAK/PXN signaling.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 30;9(1):5105. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07660-6. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30504771 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling between acto-adhesive machinery and ECM degradation in invadosomes.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(3):256-62. doi: 10.4161/cam.28558. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24727371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Diapedesis: Importance of the Transcellular Route.Adv Immunol. 2016;129:25-53. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Adv Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26791857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β3 integrin expression is required for invadopodia-mediated ECM degradation in lung carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 2;12(8):e0181579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181579. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28767724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artym V. V., Zhang Y., Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F., Yamada K. M., Mueller S. C. (2006). Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res. 66, 3034–3043 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2177 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

