Recombinant varicella-zoster virus vaccines as platforms for expression of foreign antigens
- PMID: 23843791
- PMCID: PMC3697282
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/219439
Recombinant varicella-zoster virus vaccines as platforms for expression of foreign antigens
Abstract
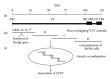
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) vaccines induce immunity against childhood chickenpox and against shingles in older adults. The safety, efficacy, and widespread use of VZV vaccines suggest that they may also be effective as recombinant vaccines against other infectious diseases that affect the young and the elderly. The generation of recombinant VZV vaccines and their evaluation in animal models are reviewed. The potential advantages and limitations of recombinant VZV vaccines are addressed.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen JI, Straus SE, Arvin AM. Varicella-zoster virus replication, pathogenesis, and management. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, et al., editors. Field's Virology. 5th edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2774–2840.
-
- Feldman S, Hughes WT, Daniel CB. Varicella in children with cancer: seventy seven cases. Pediatrics. 1975;56(3):388–397. - PubMed
-
- Wood SM, Shah SS, Steenhoff AP, Rutstein RM. Primary varicella and herpes zoster among HIV-infected children from 1989 to 2006. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):e150–e156. - PubMed
-
- Shrim A, Koren G, Farine D, et al. Management of varicella infection (chickenpox) in pregnancy. Journal of the Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. 2012;34(3):287–292. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

