Associations between the Expression of Mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6) and Clinicopathologic Parameters of Human Breast Ductal Carcinomas
- PMID: 23843846
- PMCID: PMC3706859
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2013.16.2.152
Associations between the Expression of Mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6) and Clinicopathologic Parameters of Human Breast Ductal Carcinomas
Abstract
Purpose: Mucins are members of the glycoprotein family expressed in benign and malignant epithelial cells. The aim of this study is to evaluate the relationships between the expression of mucins in breast ductal carcinoma and clinicopathologic parameters.
Methods: We constructed tumor microarrays based on 240 cases of invasive ductal carcinoma and 40 cases of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) using formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissues. We examined the expressions of MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 by immunohistochemistry.
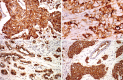
Results: MUC1 demonstrated cytoplasmic, membranous, apical, and combinative expressions. Other mucins demonstrated cytoplasmic expression. In invasive ductal carcinoma, MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 were expressed in 93.6%, 6.2%, 4.8%, and 12.4% of cases, respectively; these rates were slightly, but not significantly, higher than observed in cases of DCIS. MUC1 expression was associated with estrogen receptor (ER) expression and negative MUC1 expression was associated with triple negativity. MUC6 expression was correlated with higher histologic grade, lymphatic invasion, lymph node metastasis, and HER2 positivity. No associations with any other clinicopathologic parameters were observed.
Conclusion: Most invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast express MUC1, and this expression is associated with ER expression. MUC6 expression is correlated with some clinicopathologic parameters that are indicators of poor prognosis. To evaluate the role of MUC6 as a potential biomarker, further studies are warranted.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Human MUC1 protein; Human MUC6 protein; Mucins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between the expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) and clinicopathologic parameters of human breast carcinomas.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2020 Oct-Dec;63(4):551-558. doi: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_637_18. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33154304
-
Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC3, MUC4, MUC5AC and MUC6) and their prognostic significance in human breast cancer.Mod Pathol. 2005 Oct;18(10):1295-304. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800445. Mod Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15976813
-
Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in mucinous carcinoma of the breast: comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma.Histopathology. 2003 Jan;42(1):26-36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2003.01530.x. Histopathology. 2003. PMID: 12493022
-
Expression of mucin antigens in human cancers and its relationship with malignancy potential.Pathol Int. 1997 Dec;47(12):813-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1997.tb03713.x. Pathol Int. 1997. PMID: 9503463 Review.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of mucin family members expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 16;14:1512971. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1512971. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39886661 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunohistochemical Study of MUC1, MUC2 and MUC5AC Expression in Primary Breast Carcinoma.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Apr;11(4):EC30-EC34. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/26533.9707. Epub 2017 Apr 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28571146 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Serum Membrane-Bound Mucin-2 Levels in Breast Cancer.Biomolecules. 2019 Jan 24;9(2):40. doi: 10.3390/biom9020040. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30682816 Free PMC article.
-
Mucins as contrast agent targets for fluorescence-guided surgery of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2023 May 1;561:216150. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216150. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36997106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inverse association of rab31 and mucin-1 (CA15-3) antigen levels in estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer tissues with clinicopathological parameters and patients' prognosis.Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;7(9):1959-1970. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28979817 Free PMC article.
-
Mucin-1 Protein Is a Prognostic Marker for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Results From the CONKO-001 Study.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 27;11:670396. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.670396. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34386419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gendler SJ, Spicer AP. Epithelial mucin genes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:607–634. - PubMed
-
- Kim YS, Gum J, Jr, Brockhausen I. Mucin glycoproteins in neoplasia. Glycoconj J. 1996;13:693–707. - PubMed
-
- Fowler J, Vinall L, Swallow D. Polymorphism of the human muc genes. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D1207–D1215. - PubMed
-
- Hollingsworth MA, Swanson BJ. Mucins in cancer: protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:45–60. - PubMed
-
- Osako M, Yonezawa S, Siddiki B, Huang J, Ho JJ, Kim YS, et al. Immunohistochemical study of mucin carbohydrates and core proteins in human pancreatic tumors. Cancer. 1993;71:2191–2199. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

