Systematic review of compound danshen dropping pill: a chinese patent medicine for acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 23843882
- PMCID: PMC3703382
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/808076
Systematic review of compound danshen dropping pill: a chinese patent medicine for acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
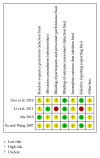
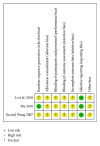
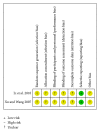
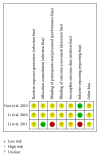
Objective. This paper systematically evaluated the efficacy and safety of compound Danshen dropping pill (CDDP) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Methods. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), comparing CDDP with no intervention, placebo, or conventional western medicine, were retrieved. Data extraction and analyses were conducted in accordance with the Cochrane standards. We assessed risk of bias for each included study and evaluated the strength of evidence on prespecified outcomes. Results. Seven RCTs enrolling 1215 patients were included. CDDP was associated with statistically significant reductions in the risk of cardiac death and heart failure compared with no intervention based on conventional therapy for AMI. In addition, CDDP was associated with improvement of quality of life and impaired left ventricular ejection fraction. Nevertheless, the safety of CDDP was unproven for the limited data. The quality of evidence for each outcome in the main comparison (CDDP versus no intervention) was "low" or "moderate." Conclusion. CDDP showed some potential benefits for AMI patients, such as the reductions of cardiac death and heart failure. However, the overall quality of evidence was poor, and the safety of CDDP for AMI patients was not confirmed. More evidence from high quality RCTs is warranted to support the use of CDDP for AMI patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Danhong Injection (a Traditional Chinese Patent Medicine) for Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:646530. doi: 10.1155/2015/646530. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26451156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of adjuvant therapy with compound danshen drip pill on inflammatory factors and cardiac function after percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 16;15:1345897. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1345897. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38689665 Free PMC article.
-
Compound Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) dripping pill for coronary heart disease: an overview of systematic reviews.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(1):25-43. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500020. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 25582415
-
[Effect of compound danshen dripping pill combined with intravenous transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells on local inflammatory response in the myocardium of rabbits with acute myocardial infarction].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;33(11):1532-7. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24483116 Chinese.
-
Long-term compound danshen dripping pills therapy reduces the no-reflow phenomenon in nondiabetes mellitus patients after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 May;9(3):1144-1151. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1056. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32498529
Cited by
-
East Wind, West Wind: Toward the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 10;16:1057817. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1057817. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36440293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Patients With Coronary Heart Disease After Treatment of Revascularization: A Prospective Cohort Study in the Northern of China.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 17;8:743262. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.743262. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34869647 Free PMC article.
-
Potential traditional Chinese medicines with anti-inflammation in the prevention of heart failure following myocardial infarction.Chin Med. 2023 Mar 17;18(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00732-w. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36932409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Acute Myocardial Infarction in Western Medicine Hospitals in China.Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2018 Mar;11(3):e004190. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.117.004190. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2018. PMID: 29848478 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive improvement of compound danshen in an Aβ25-35 peptide-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Oct 23;15:382. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0906-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26497584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- White HD, Chew DP. Acute myocardial infarction. The Lancet. 2008;372(9638):570–584. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Current concepts of the pathogenesis of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2001;104(3):365–372. - PubMed
-
- Ma X-J, Yin H-J, Chen K-J. Appraisal of the prognosis in patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2009;15(3):236–240. - PubMed
-
- Dobos G, Tao I. The model of Western integrative medicine: the role of Chinese medicine. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2011;17(1):11–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

