The role of the RACK1 ortholog Cpc2p in modulating pheromone-induced cell cycle arrest in fission yeast
- PMID: 23843946
- PMCID: PMC3701009
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065927
The role of the RACK1 ortholog Cpc2p in modulating pheromone-induced cell cycle arrest in fission yeast
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: The Role of the RACK1 Ortholog Cpc2p in Modulating Pheromone-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Fission Yeast.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 25;14(11):e0225013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225013. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31765393 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
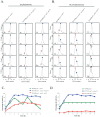
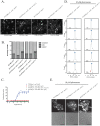
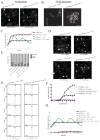
The detection and amplification of extracellular signals requires the involvement of multiple protein components. In mammalian cells the receptor of activated C kinase (RACK1) is an important scaffolding protein for signal transduction networks. Further, it also performs a critical function in regulating the cell cycle by modulating the G1/S transition. Many eukaryotic cells express RACK1 orthologs, with one example being Cpc2p in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. In contrast to RACK1, Cpc2p has been described to positively regulate, at the ribosomal level, cells entry into M phase. In addition, Cpc2p controls the stress response pathways through an interaction with Msa2p, and sexual development by modulating Ran1p/Pat1p. Here we describe investigations into the role, which Cpc2p performs in controlling the G protein-mediated mating response pathway. Despite structural similarity to Gβ-like subunits, Cpc2p appears not to function at the G protein level. However, upon pheromone stimulation, cells overexpressing Cpc2p display substantial cell morphology defects, disorientation of septum formation and a significantly protracted G1 arrest. Cpc2p has the potential to function at multiple positions within the pheromone response pathway. We provide a mechanistic interpretation of this novel data by linking Cpc2p function, during the mating response, with its previous described interactions with Ran1p/Pat1p. We suggest that overexpressing Cpc2p prolongs the stimulated state of pheromone-induced cells by increasing ste11 gene expression. These data indicate that Cpc2p regulates the pheromone-induced cell cycle arrest in fission yeast by delaying cells entry into S phase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interaction between a negative regulator (Msa2/Nrd1) and a positive regulator (Cpc2) of sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004 Jul;68(7):1621-6. doi: 10.1271/bbb.68.1621. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15277777
-
Fission yeast receptor of activated C kinase (RACK1) ortholog Cpc2 regulates mitotic commitment through Wee1 kinase.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 31;285(53):41366-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.173815. Epub 2010 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20974849 Free PMC article.
-
Cmk2 kinase is essential for survival in arsenite by modulating translation together with RACK1 orthologue Cpc2 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Dec;129:116-126. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.024. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30236788
-
The evolution of peptide mating pheromones in fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2019 Oct;65(5):1107-1111. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00968-w. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30968190 Review.
-
Pheromone Response and Mating Behavior in Fission Yeast.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2022 Dec 21;86(4):e0013022. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00130-22. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36468849 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Concern: The Role of the RACK1 Ortholog Cpc2p in Modulating Pheromone-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Fission Yeast.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 25;14(11):e0225013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225013. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31765393 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
RACK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell survival via CBR1 by suppressing TNF-α-induced ROS generation.Oncol Lett. 2016 Dec;12(6):5303-5308. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5339. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28105239 Free PMC article.
-
Parameter identification problems in the modelling of cell motility.J Math Biol. 2015 Aug;71(2):399-436. doi: 10.1007/s00285-014-0823-6. Epub 2014 Sep 2. J Math Biol. 2015. PMID: 25174444
References
-
- Gilman AG (1987) G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem 56: 615–649. - PubMed
-
- Hill C, Goddard A, Ladds G, Davey J (2009) The cationic region of Rhes mediates its interactions with specific Gbeta subunits. Cell Physiol Biochem 23: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Hiskens R, Vatish M, Hill C, Davey J, Ladds G (2005) Specific in vivo binding of activator of G protein signalling 1 to the G [beta] 1 subunit. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 2 337: 1038–1046. - PubMed
-
- Blumer JB, Cismowski MJ, Sato M, Lanier SM (2005) AGS proteins: receptor-independent activators of G-protein signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26: 470–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

