Identification of residues involved in substrate specificity and cytotoxicity of two closely related cutinases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 23843969
- PMCID: PMC3699616
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066913
Identification of residues involved in substrate specificity and cytotoxicity of two closely related cutinases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
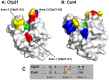
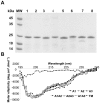
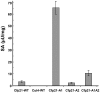
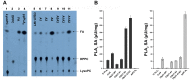
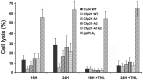
The enzymes belonging to the cutinase family are serine enzymes active on a large panel of substrates such as cutin, triacylglycerols, and phospholipids. In the M. tuberculosis H37Rv genome, seven genes coding for cutinase-like proteins have been identified with strong immunogenic properties suggesting a potential role as vaccine candidates. Two of these enzymes which are secreted and highly homologous, possess distinct substrates specificities. Cfp21 is a lipase and Cut4 is a phospholipase A2, which has cytotoxic effects on macrophages. Structural overlay of their three-dimensional models allowed us to identify three areas involved in the substrate binding process and to shed light on this substrate specificity. By site-directed mutagenesis, residues present in these Cfp21 areas were replaced by residues occurring in Cut4 at the same location. Three mutants acquired phospholipase A1 and A2 activities and the lipase activities of two mutants were 3 and 15 fold greater than the Cfp21 wild type enzyme. In addition, contrary to mutants with enhanced lipase activity, mutants that acquired phospholipase B activities induced macrophage lysis as efficiently as Cut4 which emphasizes the relationship between apparent phospholipase A2 activity and cytotoxicity. Modification of areas involved in substrate specificity, generate recombinant enzymes with higher activity, which may be more immunogenic than the wild type enzymes and could therefore constitute promising candidates for antituberculous vaccine production.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two cutinase-like proteins secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis show very different lipolytic activities reflecting their physiological function.FASEB J. 2010 Jun;24(6):1893-903. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-144766. Epub 2010 Jan 26. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20103719
-
Role of conserved active site residues in catalysis by phospholipase B1 from Cryptococcus neoformans.Biochemistry. 2007 Sep 4;46(35):10024-32. doi: 10.1021/bi7009508. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17685590
-
Exploring Covalent Allosteric Inhibition of Antigen 85C from Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Ebselen Derivatives.ACS Infect Dis. 2017 May 12;3(5):378-387. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.7b00003. Epub 2017 Mar 21. ACS Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28285521 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Triolein and Lipolytic Protein in the Pathogenesis and Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a Novel Therapeutic Approach.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;178(7):1377-89. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1953-z. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26679705 Review.
-
Phospholipase A2 enzymes: physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention.Chem Rev. 2011 Oct 12;111(10):6130-85. doi: 10.1021/cr200085w. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 21910409 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Sphingomyelinases and Phospholipases as Virulence Factors.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Jun 15;80(3):597-628. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00082-15. Print 2016 Sep. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27307578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity among Homologs of Cutinase-Like Protein Cut5 in Mycobacteria.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0133186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133186. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26177502 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible lipid accumulation and associated division arrest of Mycobacterium avium in lipoprotein-induced foamy macrophages may resemble key events during latency and reactivation of tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2014 Feb;82(2):476-90. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01196-13. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24478064 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclipostins and Cyclophostin analogs as promising compounds in the fight against tuberculosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 18;7(1):11751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11843-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28924204 Free PMC article.
-
LipG a bifunctional phospholipase/thioesterase involved in mycobacterial envelope remodeling.Biosci Rep. 2018 Dec 18;38(6):BSR20181953. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181953. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30487163 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

