Dabrafenib; preclinical characterization, increased efficacy when combined with trametinib, while BRAF/MEK tool combination reduced skin lesions
- PMID: 23844038
- PMCID: PMC3701070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067583
Dabrafenib; preclinical characterization, increased efficacy when combined with trametinib, while BRAF/MEK tool combination reduced skin lesions
Abstract
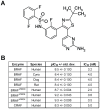
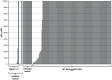
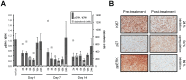
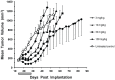
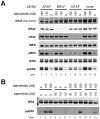
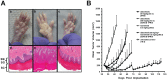
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway activation has been implicated in many types of human cancer. BRAF mutations that constitutively activate MAPK signalling and bypass the need for upstream stimuli occur with high prevalence in melanoma, colorectal carcinoma, ovarian cancer, papillary thyroid carcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma. In this report we characterize the novel, potent, and selective BRAF inhibitor, dabrafenib (GSK2118436). Cellular inhibition of BRAF(V600E) kinase activity by dabrafenib resulted in decreased MEK and ERK phosphorylation and inhibition of cell proliferation through an initial G1 cell cycle arrest, followed by cell death. In a BRAF(V600E)-containing xenograft model of human melanoma, orally administered dabrafenib inhibited ERK activation, downregulated Ki67, and upregulated p27, leading to tumor growth inhibition. However, as reported for other BRAF inhibitors, dabrafenib also induced MAPK pathway activation in wild-type BRAF cells through CRAF (RAF1) signalling, potentially explaining the squamous cell carcinomas and keratoacanthomas arising in patients treated with BRAF inhibitors. In addressing this issue, we showed that concomitant administration of BRAF and MEK inhibitors abrogated paradoxical BRAF inhibitor-induced MAPK signalling in cells, reduced the occurrence of skin lesions in rats, and enhanced the inhibition of human tumor xenograft growth in mouse models. Taken together, our findings offer preclinical proof of concept for dabrafenib as a specific and highly efficacious BRAF inhibitor and provide evidence for its potential clinical benefits when used in combination with a MEK inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition versus BRAF inhibition alone in melanoma.N Engl J Med. 2014 Nov 13;371(20):1877-88. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406037. Epub 2014 Sep 29. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25265492 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined BRAF (Dabrafenib) and MEK inhibition (Trametinib) in patients with BRAFV600-mutant melanoma experiencing progression with single-agent BRAF inhibitor.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov 20;32(33):3697-704. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.3535. Epub 2014 Oct 6. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25287827 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dabrafenib and trametinib, alone and in combination for BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 15;20(8):2035-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2054. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24583796
-
Combination dabrafenib and trametinib in the management of advanced melanoma with BRAFV600 mutations.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(7):1031-8. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2016.1168805. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27027150 Review.
-
Dabrafenib plus Trametinib: a Review in Advanced Melanoma with a BRAF (V600) Mutation.Target Oncol. 2016 Jun;11(3):417-28. doi: 10.1007/s11523-016-0443-8. Target Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27246822 Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent MEK targeted therapy prevents MAPK pathway reactivation during BRAFV600E targeted inhibition in a novel syngeneic murine glioma model.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75839-75853. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12419. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713119 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying ERK activity in response to inhibition of the BRAFV600E-MEK-ERK cascade using mathematical modelling.Br J Cancer. 2021 Nov;125(11):1552-1560. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01565-w. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34621046 Free PMC article.
-
RAF inhibitor LY3009120 sensitizes RAS or BRAF mutant cancer to CDK4/6 inhibition by abemaciclib via superior inhibition of phospho-RB and suppression of cyclin D1.Oncogene. 2018 Feb 8;37(6):821-832. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.384. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29059158
-
Therapeutic Inhibitors against Mutated BRAF and MEK for the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma.Chonnam Med J. 2017 Sep;53(3):173-177. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2017.53.3.173. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Chonnam Med J. 2017. PMID: 29026704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective anti-cancer agents as anti-aging drugs.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Dec;14(12):1092-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.27350. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 24345884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoon S, Seger R (2006) The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors 24: 21–44. - PubMed
-
- Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W (2007) MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26: 3279–3290. - PubMed
-
- Montagut C, Settleman J (2009) Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 283: 125–134. - PubMed
-
- Young A, Lyons J, Miller AL, Phan VT, Alarcon IR, et al. (2009) Ras signaling and therapies. Adv Cancer Res 102: 1–17. - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AM, Robert C (2011) New drugs in melanoma: it's a whole new world. Eur J Cancer 47: 2150–2157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

