Jejunojejunal Intussusception as the Initial Presentation of Non-Hodgkin's B-Cell Lymphoma in an Adult Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 23844307
- PMCID: PMC3703414
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/619031
Jejunojejunal Intussusception as the Initial Presentation of Non-Hodgkin's B-Cell Lymphoma in an Adult Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
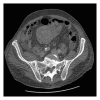
Introduction. Intussusception is a rare cause of bowel obstruction in adults and is usually associated with an underlying pathology, benign, or malignant. This is a report of a case of jejunojejunal intussusception secondary to non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma in an adult patient. Case Presentation. A 74-year-old male with no previous significant medical history presented with symptoms of acute intestinal obstruction. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis revealed 2 areas of jejunojejunal intussusception, which were surgically managed successfully. Histopathological examination of the specimen revealed the presence of high grade diffuse large B-cell-type non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and the patient was referred to the oncology team for further management. Discussion. B-cell lymphoma is a rare but well-documented cause of intussusception in adults, with most cases being at the ileocolic region. We present a rare case of jejunojejunal intussusception as the initial presentation of non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma in an adult patient.
Figures
References
-
- Akbulut S. Unusual cause of adult intussusception: diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a case report and review. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2012;16:1938–1946. - PubMed
-
- Salemis NS, Tsiambas E, Liatsos C, Karameris A, Tsohataridis E. Small bowel intussusception due to a primary non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. An unusual presentation and clinical course. Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer. 2010;41(4):233–237. - PubMed
-
- Ford EG. Gastrointestinal tumors. In: Andrassy RJ, editor. Pediatric Surgical Oncology. 1st edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: WB Saunders; 1998. pp. 289–304.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources