Autocrine IGF-I/insulin receptor axis compensates for inhibition of AKT in ER-positive breast cancer cells with resistance to estrogen deprivation
- PMID: 23844554
- PMCID: PMC3979036
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3449
Autocrine IGF-I/insulin receptor axis compensates for inhibition of AKT in ER-positive breast cancer cells with resistance to estrogen deprivation
Abstract
Introduction: Estrogen receptor α-positive (ER+) breast cancers adapt to hormone deprivation and acquire resistance to antiestrogen therapies. Upon acquisition of hormone independence, ER+ breast cancer cells increase their dependence on the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. We examined the effects of AKT inhibition and its compensatory upregulation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I/InsR signaling in ER+ breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to estrogen deprivation.
Methods: Inhibition of AKT using the catalytic inhibitor AZD5363 was examined in four ER+ breast cancer cell lines resistant to long-term estrogen deprivation (LTED) by western blotting and proliferation assays. Feedback upregulation and activation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) was examined by western blotting, real-time qPCR, ELISAs, membrane localization of AKT PH-GFP by immunofluorescence and phospho-RTK arrays. For studies in vivo, athymic mice with MCF-7 xenografts were treated with AZD5363 and fulvestrant with either the ATP-competitive IGF-IR/InsR inhibitor AZD9362 or the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor AZD4547.
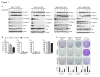
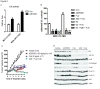
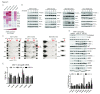
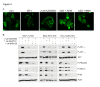
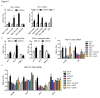
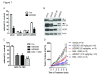
Results: Treatment with AZD5363 reduced phosphorylation of the AKT/mTOR substrates PRAS40, GSK3α/β and S6K while inducing hyperphosphorylation of AKT at T308 and S473. Inhibition of AKT with AZD5363 suppressed growth of three of four ER+ LTED lines and prevented emergence of hormone-independent MCF-7, ZR75-1 and MDA-361 cells. AZD5363 suppressed growth of MCF-7 xenografts in ovariectomized mice and a patient-derived luminal B xenograft unresponsive to tamoxifen or fulvestrant. Combined treatment with AZD5363 and fulvestrant suppressed MCF-7 xenograft growth better than either drug alone. Inhibition of AKT with AZD5363 resulted in upregulation and activation of RTKs, including IGF-IR and InsR, upregulation of FoxO3a and ERα mRNAs as well as FoxO- and ER-dependent transcription of IGF-I and IGF-II ligands. Inhibition of IGF-IR/InsR or PI3K abrogated AKT PH-GFP membrane localization and T308 P-AKT following treatment with AZD5363. Treatment with IGFBP-3 blocked AZD5363-induced P-IGF-IR/InsR and T308 P-AKT, suggesting that receptor phosphorylation was dependent on increased autocrine ligands. Finally, treatment with the dual IGF-IR/InsR inhibitor AZD9362 enhanced the anti-tumor effect of AZD5363 in MCF-7/LTED cells and MCF-7 xenografts in ovariectomized mice devoid of estrogen supplementation.
Conclusions: These data suggest combinations of AKT and IGF-IR/InsR inhibitors would be an effective treatment strategy against hormone-independent ER+ breast cancer.
Figures
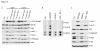
References
-
- Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A, Testa JR. Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 2005;15:29–86. - PubMed
-
- Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, Donoho GP, Briggs SL, Robbins CM, Hostetter G, Boguslawski S, Moses TY, Savage S, Uhlik M, Lin A, Du J, Qian YW, Zeckner DJ, Tucker-Kellogg G, Touchman J, Patel K, Mousses S, Bittner M, Schevitz R, Lai MH, Blanchard KL, Thomas JE. A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature. 2007;15:439–444. doi: 10.1038/nature05933. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

