novel modifications on C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II can fine-tune the phosphatase activity of Ssu72
- PMID: 23844594
- PMCID: PMC4296584
- DOI: 10.1021/cb400229c
novel modifications on C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II can fine-tune the phosphatase activity of Ssu72
Abstract
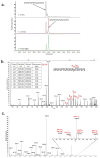
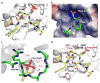
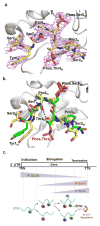
The C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II (CTD) modulates the process of transcription through sequential phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of its heptide repeats, through which it recruits various transcription regulators. Ssu72 is the first characterized cis-specific CTD phosphatase that dephosphorylates Ser5 with a requirement for the adjacent Pro6 in a cis conformation. The recent discovery of Thr4 phosphorylation in the CTD calls into question whether such a modification can interfere with Ssu72 binding via the elimination of a conserved intramolecular hydrogen bond in the CTD that is potentially essential for recognition. To test if Thr4 phosphorylation will abolish Ser5 dephosphorylation by Ssu72, we determined the kinetic and structural properties of Drosophila Ssu72-symplekin in complex with the CTD peptide with consecutive phosphorylated Thr4 and Ser5. Our mass spectrometric and kinetic data established that Ssu72 does not dephosphorylate Thr4, but the existence of phosphoryl-Thr4 next to Ser5 reduces the activity of Ssu72 toward the CTD peptide by 4-fold. To our surprise, even though the intramolecular hydrogen bond is eliminated due to the phosphorylation of Thr4, the CTD adopts an almost identical conformation to be recognized by Ssu72 with Ser5 phosphorylated alone or both Thr4/Ser5 phosphorylated. Our results indicate that Thr4 phosphorylation will not abolish the essential Ssu72 activity, which is needed for cell survival. Instead, the phosphatase activity of Ssu72 is fine-tuned by Thr4 phosphorylation and eventually may lead to changes in transcription. Overall, we report the first case of structural and kinetic effects of phosphorylated Thr4 on CTD modifying enzymes. Our results support a model in which a combinatorial cascade of CTD modification can modulate transcription.
Figures
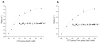
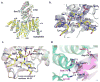
Similar articles
-
Structural determinants for accurate dephosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by its cognate C-terminal domain (CTD) phosphatase during eukaryotic transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 24;294(21):8592-8605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007697. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30971428 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of Ssu72, an essential eukaryotic phosphatase specific for the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, in complex with a transition state analogue.Biochem J. 2011 Mar 15;434(3):435-44. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101471. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21204787
-
Crystal structure of the human symplekin-Ssu72-CTD phosphopeptide complex.Nature. 2010 Oct 7;467(7316):729-33. doi: 10.1038/nature09391. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20861839 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse and conserved roles of the protein Ssu72 in eukaryotes: from yeast to higher organisms.Curr Genet. 2021 Apr;67(2):195-206. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01132-5. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33244642 Review.
-
Dynamic phosphorylation patterns of RNA polymerase II CTD during transcription.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.013. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982363 Review.
Cited by
-
Photodissociation mass spectrometry: new tools for characterization of biological molecules.Chem Soc Rev. 2014 Apr 21;43(8):2757-83. doi: 10.1039/c3cs60444f. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Chem Soc Rev. 2014. PMID: 24481009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Tools for Studying the Impact of cis/trans Prolyl Isomerization on Signaling: A Case Study on RNA Polymerase II Phosphatase Activity and Specificity.Methods Enzymol. 2018;607:269-297. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2018.04.020. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Methods Enzymol. 2018. PMID: 30149861 Free PMC article.
-
Ultraviolet photodissociation for characterization of whole proteins on a chromatographic time scale.Anal Chem. 2014 Feb 18;86(4):2185-92. doi: 10.1021/ac403859a. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Anal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24447299 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants for accurate dephosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by its cognate C-terminal domain (CTD) phosphatase during eukaryotic transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 24;294(21):8592-8605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007697. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30971428 Free PMC article.
-
Dephosphorylating eukaryotic RNA polymerase II.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Apr;1864(4):372-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26779935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dahmus ME. Reversible phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:19009–19012. - PubMed
-
- Meinhart A, Silberzahn T, Cramer P. The mRNA Transcription/Processing Factor Ssu72 Is a Potential Tyrosine Phosphatase. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278:15917–15921. - PubMed
-
- Palancade B, Bensaude O. Investigating RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 2003;270:3859–3870. - PubMed
-
- Egloff S, Dienstbier M, Murphy S. Updating the RNA polymerase CTD code: adding gene-specific layers. Trends Genet. 2012;28:333–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

