Molecular mechanisms of the crosstalk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidase through reactive oxygen species-studies in white blood cells and in animal models
- PMID: 23845067
- PMCID: PMC3887465
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2012.4953
Molecular mechanisms of the crosstalk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidase through reactive oxygen species-studies in white blood cells and in animal models
Abstract
Aims: Oxidative stress is involved in the development of cardiovascular disease. There is a growing body of evidence for a crosstalk between different enzymatic sources of oxidative stress. With the present study, we sought to determine the underlying crosstalk mechanisms, the role of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), and its link to endothelial dysfunction.
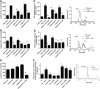
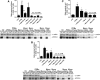
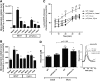
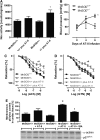
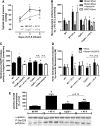
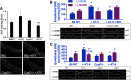
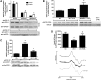
Results: NADPH oxidase (Nox) activation (oxidative burst and translocation of cytosolic Nox subunits) was observed in response to mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) formation in human leukocytes. In vitro, mtROS-induced Nox activation was prevented by inhibitors of the mPTP, protein kinase C, tyrosine kinase cSrc, Nox itself, or an intracellular calcium chelator and was absent in leukocytes with p47phox deficiency (regulates Nox2) or with cyclophilin D deficiency (regulates mPTP). In contrast, the crosstalk in leukocytes was amplified by mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (type 2) (MnSOD(+/-)) deficiency. In vivo, increases in blood pressure, degree of endothelial dysfunction, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) dysregulation/uncoupling (e.g., eNOS S-glutathionylation) or Nox activity, p47phox phosphorylation in response to angiotensin-II (AT-II) in vivo treatment, or the aging process were more pronounced in MnSOD(+/-) mice as compared with untreated controls and improved by mPTP inhibition by cyclophilin D deficiency or sanglifehrin A therapy.
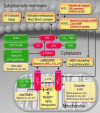
Innovation: These results provide new mechanistic insights into what extent mtROS trigger Nox activation in phagocytes and cardiovascular tissue, leading to endothelial dysfunction.
Conclusions: Our data show that mtROS trigger the activation of phagocytic and cardiovascular NADPH oxidases, which may have fundamental implications for immune cell activation and development of AT-II-induced hypertension.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nox4 NADPH oxidase mediates peroxynitrite-dependent uncoupling of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase and fibronectin expression in response to angiotensin II: role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 4;288(40):28668-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470971. Epub 2013 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23940049 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin D-mediated angiotensin II-induced NADPH oxidase 4 activation in endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction that can be rescued by gallic acid.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 5;940:175475. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175475. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36563952
-
Nox2-induced production of mitochondrial superoxide in angiotensin II-mediated endothelial oxidative stress and hypertension.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jan 10;20(2):281-94. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4918. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24053613 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Oct 1;51(7):1289-301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.033. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21777669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox signaling (cross-talk) from and to mitochondria involves mitochondrial pores and reactive oxygen species.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jun-Jul;1797(6-7):897-906. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.01.032. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20122895 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordinated Contribution of NADPH Oxidase- and Mitochondria-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic Syndrome and Its Implication in Renal Dysfunction.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 4;12:670076. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.670076. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34017260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NADPH oxidases and oxidase crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases: novel therapeutic targets.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 Mar;17(3):170-194. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0260-8. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31591535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Redox Signaling, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling, and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Setting of Transportation Noise Exposure or Chronic Treatment with Organic Nitrates.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 May;38(13-15):1001-1021. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0006. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36719770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PGC1α Regulates the Endothelial Response to Fluid Shear Stress via Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Control of Heme Oxygenase-1.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022 Jan;42(1):19-34. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.317066. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022. PMID: 34789002 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp70 Suppresses Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Preserves Pulmonary Microvascular Barrier Integrity Following Exposure to Bacterial Toxins.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 12;9:1309. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01309. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29951058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balsari A, Marolda R, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Sciorelli G, Tona G, Cosulich E, Taramelli D, Fossati G, Parmiani G, and Cascinelli N. Systemic administration of autologous, alloactivated helper-enriched lymphocytes to patients with metastatic melanoma of the lung. A phase I study. Cancer Immunol Immunother 21: 148–155, 1986 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basso E, Fante L, Fowlkes J, Petronilli V, Forte MA, and Bernardi P. Properties of the permeability transition pore in mitochondria devoid of Cyclophilin D. J Biol Chem 280: 18558–18561, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

