PRECISE - pregabalin in addition to usual care for sciatica: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 23845078
- PMCID: PMC3711833
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-213
PRECISE - pregabalin in addition to usual care for sciatica: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Sciatica is a type of neuropathic pain that is characterised by pain radiating into the leg. It is often accompanied by low back pain and neurological deficits in the lower limb. While this condition may cause significant suffering for the individual, the lack of evidence supporting effective treatments for sciatica makes clinical management difficult. Our objectives are to determine the efficacy of pregabalin on reducing leg pain intensity and its cost-effectiveness in patients with sciatica.
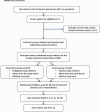
Methods/design: PRECISE is a prospectively registered, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial of pregabalin compared to placebo, in addition to usual care. Inclusion criteria include moderate to severe leg pain below the knee with evidence of nerve root/spinal nerve involvement. Participants will be randomised to receive either pregabalin with usual care (n = 102) or placebo with usual care (n = 102) for 8 weeks. The medicine dosage will be titrated up to the participant's optimal dose, to a maximum 600 mg per day. Follow up consultations will monitor individual progress, tolerability and adverse events. Usual care, if deemed appropriate by the study doctor, may include a referral for physical or manual therapy and/or prescription of analgesic medication. Participants, doctors and researchers collecting participant data will be blinded to treatment allocation. Participants will be assessed at baseline and at weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 26 and 52. The primary outcome will determine the efficacy of pregabalin in reducing leg pain intensity. Secondary outcomes will include back pain intensity, disability and quality of life. Data analysis will be blinded and by intention-to-treat. A parallel economic evaluation will be conducted from health sector and societal perspectives.
Discussion: This study will establish the efficacy of pregabalin in reducing leg pain intensity in patients with sciatica and provide important information regarding the effect of pregabalin treatment on disability and quality of life. The impact of this research may allow the future development of a cost-effective conservative treatment strategy for patients with sciatica.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrial.gov, ACTRN 12613000530729.
References
-
- Haanpää M, Treede RD. Diagnosis and classification of neuropathic pain epidemiology and impact of neuropathic pain. Pain Clinical Updates. 2010;18:1–6.
-
- Attal N, Finnerup NB. Pharmacological management of neuropathic pain. Pain Clinical Updates. 2010;18:1–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical