Advances in parametric mapping with CMR imaging
- PMID: 23845576
- PMCID: PMC4073213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.05.005
Advances in parametric mapping with CMR imaging
Erratum in
- JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Aug;6(8):929-30
Abstract
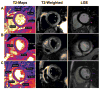
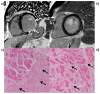
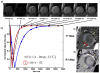
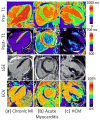
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) is well established and considered the gold standard for assessing myocardial volumes and function, and for quantifying myocardial fibrosis in both ischemic and nonischemic heart disease. Recent developments in CMR imaging techniques are enabling clinically-feasible rapid parametric mapping of myocardial perfusion and magnetic relaxation properties (T1, T2, and T2* relaxation times) that are further expanding the range of unique tissue parameters that can be assessed using CMR. To generate a parametric map of perfusion or relaxation times, multiple images of the same region of the myocardium are acquired with different sensitivity to the parameter of interest, and the signal intensities of these images are fit to a model which describes the underlying physiology or relaxation parameters. The parametric map is an image of the fitted perfusion parameters or relaxation times. Parametric mapping requires acquisition of multiple images typically within a breath-hold and thus requires specialized rapid acquisition techniques. Quantitative perfusion imaging techniques can more accurately determine the extent of myocardial ischemia in coronary artery disease and provide the opportunity to evaluate microvascular disease with CMR. T1 mapping techniques performed both with and without contrast are enabling quantification of diffuse myocardial fibrosis and myocardial infiltration. Myocardial edema and inflammation can be evaluated using T2 mapping techniques. T2* mapping provides an assessment of myocardial iron-overload and myocardial hemorrhage. There is a growing body of evidence for the clinical utility of quantitative assessment of perfusion and relaxation times, although current techniques still have some important limitations. This article will review the current imaging technologies for parametric mapping, emerging applications, current limitations, and potential of CMR parametric mapping of the myocardium. The specific focus will be the assessment and quantification of myocardial perfusion and magnetic relaxation times.
Copyright © 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Evolution and revolution in CMR imaging.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Jul;6(7):837-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.05.007. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23845577 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lorenz CH, Walker ES, Morgan VL, Klein SS, Graham TP., Jr Normal human right and left ventricular mass, systolic function, and gender differences by cine magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 1999;1:7–21. - PubMed
-
- Iles L, Pfluger H, Phrommintikul A, et al. Evaluation of diffuse myocardial fibrosis in heart failure with cardiac magnetic resonance contrast-enhanced T1 mapping. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1574–80. - PubMed
-
- Flett AS, Hayward MP, Ashworth MT, et al. Equilibrium contrast cardiovascular magnetic resonance for the measurement of diffuse myocardial fibrosis: preliminary validation in humans. Circulation. 2010;122:138–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

