Surfactant reduction of cerebral infarct size and behavioral deficit in a rat model of cerebrovascular arterial gas embolism
- PMID: 23845977
- PMCID: PMC3764619
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01382.2012
Surfactant reduction of cerebral infarct size and behavioral deficit in a rat model of cerebrovascular arterial gas embolism
Abstract
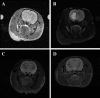
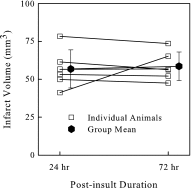
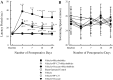
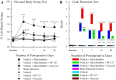
Gas embolism occurs commonly in cardiac and vascular surgery and decompression sickness. The goals of this study were to develop a new in vivo rat model of cerebrovascular arterial gas embolism and to determine the effects of exogenous surfactants on resultant brain infarct volume and accompanying long-term neurological dysfunction using the model. Unilateral cerebral arterial gas embolism was induced in Sprague Dawley rats, including groups receiving intravenous Pluronic F-127 (PF-127) and Oxycyte perflourocarbon surfactant pretreatment. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed at 24 and 72 h postembolism to determine infarct volume. The elevated body swing test (EBST), limb-placement test, proprioception forelimb and hindlimb tests, whisker tactile test, and Morris Water Maze test were performed to assess motor behavior, somatosensory deficit, and spatial cognitive function out to 29 days after embolization. A stable stroke model was developed with MRI examination revealing infarction in the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere. Gas embolized rats had significant cognitive and sensorimotor dysfunction, including approximately threefold increase in Morris Water Maze latency time, ∼20% left-sided biasing in EBST performance, 0.5 to 1.5 (mean) point score elevations in the proprioception and whisker tactile tests, and 3.0 point (mean) elevation in the limb-placement test, all of which were persistent throughout the postembolic period. Surfactant prophylaxis with either PF-127 or Oxycyte rendered stroke undetectable by MRI scanning and markedly reduced the postembolic deficits in both cognitive and sensorimotor performance in treated rats, with normalization of EBST and whisker tactile tests within 7 days.
Keywords: animal; behavior; cognition; experimental; gas embolism; rat; stroke; surfactant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurological dysfunctions versus regional infarction volume after focal ischemia in Mongolian gerbils.Stroke. 2003 Jun;34(6):1501-6. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000074034.32371.13. Epub 2003 May 15. Stroke. 2003. PMID: 12750539
-
A comparison of long-term functional outcome after 2 middle cerebral artery occlusion models in rats.Stroke. 2001 Nov;32(11):2648-57. doi: 10.1161/hs1101.097397. Stroke. 2001. PMID: 11692030
-
Influence of endothelial glycocalyx degradation and surfactants on air embolism adhesion.Anesthesiology. 2006 Dec;105(6):1220-7. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200612000-00022. Anesthesiology. 2006. PMID: 17122585
-
Enhanced neocortical neural sprouting, synaptogenesis, and behavioral recovery with D-amphetamine therapy after neocortical infarction in rats.Stroke. 1998 Nov;29(11):2381-93; discussion 2393-5. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.11.2381. Stroke. 1998. PMID: 9804653
-
Gas embolism and surfactant-based intervention: implications for long-duration space-based activity.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Sep;1077:256-69. doi: 10.1196/annals.1362.039. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17124129 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical Validation of the Therapeutic Potential of Glasgow Oxygen Level Dependent (GOLD) Technology: a Theranostic for Acute Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2019 Oct;10(5):583-595. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0679-y. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Transl Stroke Res. 2019. PMID: 30506268 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated body swing test after focal cerebral ischemia in rodents: methodological considerations.BMC Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;16:50. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0189-8. BMC Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26242584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Omar Y, Balacumaraswami L, Pigott DW, Matthews PM, Taggart DP. Solid and gaseous cerebral microembolization during off-pump, on-pump, and open cardiac surgery procedures. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 127: 1759–1765, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Andersen M, Overgaard K, Meden P, Boysen G. Effects of citicoline combined with thrombolytic therapy in a rat embolic stroke model. Stroke 30: 1464–1471, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Ayyaswamy PS, Zhang J, Eckmann DM. Numerical modeling of the transport to an intravascular bubble in a tube with a soluble/insoluble surfactant. Ann NY Acad Sci 1077: 270–287, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Branger AB, Eckmann DM. Theoretical and experimental intravascular gas embolism absorption dynamics. J Appl Physiol 87: 1287–1295, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

