Daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, ameliorates postoperative ileus by anti-inflammatory action through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- PMID: 23846546
- PMCID: PMC4048467
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-013-0854-6
Daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, ameliorates postoperative ileus by anti-inflammatory action through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Abstract
Background: Daikenchuto (DKT), a gastrointestinal prokinetic Japanese herbal medicine, is prescribed for patients with postoperative ileus (POI) and adhesive bowel obstruction following abdominal surgery. Several mechanisms for the amelioration of POI by DKT have been suggested; however, it has remained unclear whether DKT shows anti-inflammatory effects in POI. In the present study, we investigated the effects of DKT in a mouse POI model and attempted to clarify the detailed mechanisms of action.
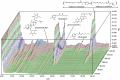
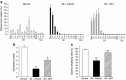
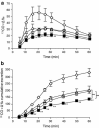
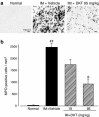
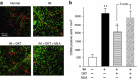
Method: Intestinal manipulation (IM) was applied to the distal ileum of mice. DKT was administered orally to the animals 4 times before and after IM. Gastrointestinal transit in vivo, leukocyte infiltration, cytokine mRNA expression and gastrointestinal motility were analyzed. We also investigated the effects of the α7nAChR antagonist methyllycaconitine citrate (MLA) on the DKT-mediated ameliorative action against POI, and we studied the effects of DKT on inflammatory activity in α7nAChR knockout mice.
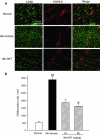
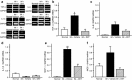
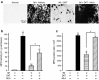
Results: DKT treatment led to recovery of the delayed intestinal transit induced by IM. DKT significantly inhibited the infiltration of neutrophils and CD68-positive macrophages, and inhibited mRNA expressions of TNF-α and MCP-1. MLA significantly reduced the anti-inflammatory action of DKT, and the amelioration of macrophage infiltration by DKT was partially suppressed in α7nAChR knockout mice.
Conclusions: In conclusion, in addition to the gastrointestinal prokinetic action, DKT serves as a novel therapeutic agent for POI characterized by its anti-inflammatory potency. The DKT-induced anti-inflammatory activity may be partly mediated by activation of α7nAChR.
Figures
References
-
- Tsuchida Y, Hatao F, Fujisawa M, Murata T, Kaminishi M, Seto Y, et al. Neuronal stimulation with 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor induces anti-inflammatory actions via alpha7nACh receptors on muscularis macrophages associated with postoperative ileus. Gut. 2011;60(5):638–647. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.227546. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

