Lipidosterolic extract of serenoa repens modulates the expression of inflammation related-genes in benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial and stromal cells
- PMID: 23846725
- PMCID: PMC3742245
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140714301
Lipidosterolic extract of serenoa repens modulates the expression of inflammation related-genes in benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial and stromal cells
Abstract
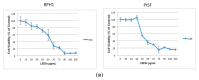
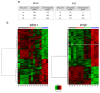
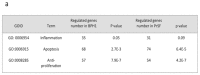
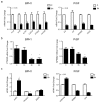
Despite the high prevalence of histological Benign Prostatic Hypeplasia (BPH) in elderly men, little is known regarding the molecular mechanisms and networks underlying the development and progression of the disease. Here, we explored the effects of a phytotherapeutic agent, Lipidosterolic extract of the dwarf palm plant Serenoa repens (LSESr), on the mRNA gene expression profiles of two representative models of BPH, BPH1 cell line and primary stromal cells derived from BPH. Treatment of these cells with LSESr significantly altered gene expression patterns as assessed by comparative gene expression profiling on gene chip arrays. The expression changes were manifested three hours following in vitro administration of LSESr, suggesting a rapid action for this compound. Among the genes most consistently affected by LSESr treatment, we found numerous genes that were categorized as part of proliferative, apoptotic, and inflammatory pathways. Validation studies using quantitative real-time PCR confirmed the deregulation of genes known to exhibit key roles in these biological processes including IL1B, IL1A, CXCL6, IL1R1, PTGS2, ALOX5, GAS1, PHLDA1, IL6, IL8, NFkBIZ, NFKB1, TFRC, JUN, CDKN1B, and ERBB3. Subsequent analyses also indicated that LSESr treatment can impede the stimulatory effects of certain proinflammatory cytokines such as IL6, IL17, and IL15 in these cells. These results suggest that LSESr may be useful to treat BPH that manifest inflammation characteristics. This also supports a role for inflammation in BPH presumably by mediating the balance between apoptosis and proliferation.
Figures


References
-
- Carter H.B., Coffey D.S. The prostate: An increasing medical problem. Prostate. 1990;16:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Lee K.L., Peehl D.M. Molecular and cellular pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2004;172:1784–1791. - PubMed
-
- Kramer G., Mitteregger D., Marberger M. Is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) an immune inflammatory disease? Eur. Urol. 2007;51:1202–1216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

