Inference of alternative splicing from RNA-Seq data with probabilistic splice graphs
- PMID: 23846746
- PMCID: PMC3753571
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt396
Inference of alternative splicing from RNA-Seq data with probabilistic splice graphs
Abstract
Motivation: Alternative splicing and other processes that allow for different transcripts to be derived from the same gene are significant forces in the eukaryotic cell. RNA-Seq is a promising technology for analyzing alternative transcripts, as it does not require prior knowledge of transcript structures or genome sequences. However, analysis of RNA-Seq data in the presence of genes with large numbers of alternative transcripts is currently challenging due to efficiency, identifiability and representation issues.
Results: We present RNA-Seq models and associated inference algorithms based on the concept of probabilistic splice graphs, which alleviate these issues. We prove that our models are often identifiable and demonstrate that our inference methods for quantification and differential processing detection are efficient and accurate.
Availability: Software implementing our methods is available at http://deweylab.biostat.wisc.edu/psginfer.
Contact: cdewey@biostat.wisc.edu
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
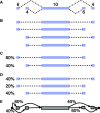
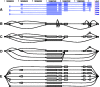
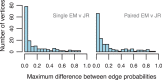
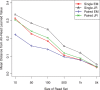
 , sign test) except for that between Single EM and Paired JR for read set size = 10
, sign test) except for that between Single EM and Paired JR for read set size = 10References
-
- Bohnert R, et al. Transcript quantification with RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10(Suppl. 13):P5.
-
- Chang H, et al. The application of alternative splicing graphs in quantitative analysis of alternative splicing form from EST database. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2005;22:14–22.
-
- Dye MJ, et al. Exon tethering in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell. 2006;21:849–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

