Impaired direct priming of CD8 T cells by donor-derived cytomegalovirus following kidney transplantation
- PMID: 23847277
- PMCID: PMC3785283
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013040340
Impaired direct priming of CD8 T cells by donor-derived cytomegalovirus following kidney transplantation
Abstract
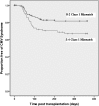
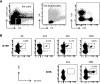
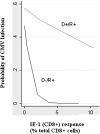
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection increases the risk of complications after renal transplantation, but the mechanisms controlling donor-derived infection are not adequately characterized. Here, we assessed the risk of clinically significant CMV disease in donor-seropositive, recipient-seropositive (D+R+) renal transplantation and examined recipients' CMV antigen-specific cellular immune responses primed directly by donor cells. In a retrospective cohort of 569 patients administered standardized basiliximab-tacrolimus-mycophenolate-corticosteroid immunosuppressive therapy, CMV disease rates increased in D+R+ serostatus pairings compared with D-R+ pairings (hazard ratio [HR], 2.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.36 to 5.01; P=0.004) and associated with increased donor-recipient HLA mismatch in the D+R+ group (HR [per class 1 mismatch], 1.43; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.82]; P=0.02). D+R+ and D+R- transplants in which the donor and recipient differentially expressed at least one HLA class I allele were followed prospectively from the time of transplantation. During the first year after transplantation, four of eight seropositive recipients and one of three seronegative recipients displayed peripheral blood CD8+ T cell responses to CMV presented by recipient-specific HLA. Notably, no recipients mounted responses to CMV presented by donor-specific HLA, despite the detection of CMV antigen expression in all seropositive donor organs examined (n=10), suggesting that the allograft of Class I HLA-mismatched seropositive donors is inaccessible to CD8+ T cell responses. Finally, pretransplant assays of anti-CMV cellular immunity predicted post-transplant CMV replication less accurately in D+R+ pairings than in D-R+ pairings, possibly reflecting in vitro assay specificity for recipient, rather than donor, HLA. These findings are relevant to the clinical management and immunologic understanding of donor-transmitted viral infection.
Figures


References
-
- Moss P, Khan N: CD8(+) T-cell immunity to cytomegalovirus. Hum Immunol 65: 456–464, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Grundy JE, Lui SF, Super M, Berry NJ, Sweny P, Fernando ON, Moorhead J, Griffiths PD. Symptomatic cytomegalovirus infection in seropositive kidney recipients: Reinfection with donor virus rather than reactivation of recipient virus. Lancet 1988. 16;2(8603):132-5. - PubMed
-
- Kliem V, Fricke L, Wollbrink T, Burg M, Radermacher J, Rohde F: Improvement in long-term renal graft survival due to CMV prophylaxis with oral ganciclovir: Results of a randomized clinical trial. Am J Transplant 8: 975–983, 2008 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

