CD49b/CD69-Dependent Generation of Resting T Helper Cell Memory
- PMID: 23847623
- PMCID: PMC3706785
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00183
CD49b/CD69-Dependent Generation of Resting T Helper Cell Memory
Abstract
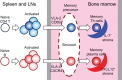
In the absence of antigen, memory T helper (Th) cells are maintained in a resting state. Recently it has been shown that bone marrow (BM) is a major reservoir of resting memory Th cells. In a given immune response, less than 10% of the activated CD4 T cells are recruited to the pool of resting BM memory Th cells. Here we review recent evidence that CD69 and CD49b control homing of memory Th cell precursors to the BM. During the effector phase of an immune response, about 10% of activated CD4 T cells in the spleen express both CD69 and CD49b, and thus qualify as precursors of resting memory Th cells of BM. Loss or blockade of CD69 and CD49b expression on CD4 T cells impairs the generation of resting memory Th cells in the BM. Moreover, in the absence of BM memory Th cells in CD69-deficient mice, T-cell help for B cells is impaired, confirming the central role of BM memory Th cells in the maintenance of immunological memory.
Keywords: CD49b; CD69; T helper cells; bone marrow; homing; immunological memory.
Figures
References
-
- Radbruch A, Rajewsky K. The cellular basis of B cell memory. In: Frederick W, Alt TH, Michael SN. editors. The Molecular Biology of B Cells. London: Elsevier Science; (2004). p. 247–59
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials