Synthetic approaches to study transcriptional networks and noise in mammalian systems
- PMID: 23848051
- PMCID: PMC8687214
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-syb.2012.0026
Synthetic approaches to study transcriptional networks and noise in mammalian systems
Abstract
Synthetic biology aims to build new functional organisms and to rationally re-design existing ones by applying the engineering principle of modularity. Apart from building new life forms to perform technical applications, the approach of synthetic biology is useful to dissect complex biological phenomena into simple and easy to understand synthetic modules. Synthetic gene networks have been successfully implemented in prokaryotes and lower eukaryotes, with recent approaches moving ahead towards the mammalian environment. However, synthetic circuits in higher eukaryotes present a more challenging scenario, since its reliability is compromised because of the strong stochastic nature of transcription. Here, the authors review recent approaches that take advantage of the noisy response of synthetic regulatory circuits to learn key features of the complex machinery that orchestrates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Understanding the causes and consequences of biological noise will allow us to design more reliable mammalian synthetic circuits with revolutionary medical applications.
Figures
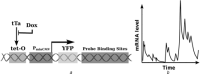
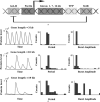
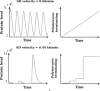
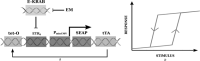
Similar articles
-
Experimental measurements and mathematical modeling of biological noise arising from transcriptional and translational regulation of basic synthetic gene circuits.J Theor Biol. 2016 Apr 21;395:153-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Theor Biol. 2016. PMID: 26874228
-
Synthetic biological networks.Rep Prog Phys. 2013 Sep;76(9):096602. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/76/9/096602. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2013. PMID: 24006369 Review.
-
Synthetic biology: insights into biological computation.Integr Biol (Camb). 2016 Apr 18;8(4):518-32. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00274e. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Integr Biol (Camb). 2016. PMID: 27074335 Review.
-
Controlling cell-to-cell variability with synthetic gene circuits.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Dec 20;47(6):1795-1804. doi: 10.1042/BST20190295. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31803907 Review.
-
Inducible gene expression: diverse regulatory mechanisms.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Jun;11(6):426-37. doi: 10.1038/nrg2781. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 20421872 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

