Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling: a functional perspective
- PMID: 23848055
- PMCID: PMC3904253
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12296
Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling: a functional perspective
Abstract
Multiple homeostatic systems are regulated by orexin (hypocretin) peptides and their two known GPCRs. Activation of orexin receptors promotes waking and is essential for expression of normal sleep and waking behaviour, with the sleep disorder narcolepsy resulting from the absence of orexin signalling. Orexin receptors also influence systems regulating appetite/metabolism, stress and reward, and are found in several peripheral tissues. Nevertheless, much remains unknown about the signalling pathways and targets engaged by native receptors. In this review, we integrate knowledge about the orexin receptor signalling capabilities obtained from studies in expression systems and various native cell types (as presented in Kukkonen and Leonard, this issue of British Journal of Pharmacology) with knowledge of orexin signalling in different tissues. The tissues reviewed include the CNS, the gastrointestinal tract, the pituitary gland, pancreas, adrenal gland, adipose tissue and the male reproductive system. We also summarize the findings in different native and recombinant cell lines, especially focusing on the different cascades in CHO cells, which is the most investigated cell line. This reveals that while a substantial gap exists between what is known about orexin receptor signalling and effectors in recombinant systems and native systems, mounting evidence suggests that orexin receptor signalling is more diverse than originally thought. Moreover, rather than being restricted to orexin receptor 'overexpressing' cells, this signalling diversity may be utilized by native receptors in a site-specific manner.
Keywords: adipose tissue; adrenal gland; cell death; depolarization; hormone release; hypocretin; neuron; orexin; plasticity; second messenger.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
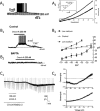

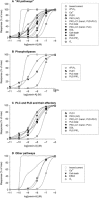
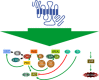
Comment on
-
Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling cascades.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;171(2):314-31. doi: 10.1111/bph.12324. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23902572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Vandermaelen CP. Intracellular recordings from serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons: pacemaker potentials and the effect of LSD. Brain Res. 1982;238:463–469. - PubMed
-
- Ammoun S, Holmqvist T, Shariatmadari R, Oonk HB, Detheux M, Parmentier M, et al. Distinct recognition of OX1 and OX2 receptors by orexin peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:507–514. - PubMed
-
- Ammoun S, Johansson L, Ekholm ME, Holmqvist T, Danis AS, Korhonen L, et al. OX1 orexin receptors activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in CHO cells via multiple mechanisms: the role of Ca2+ influx in OX1 receptor signaling. Mol Endocrinol. 2006a;20:80–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

