The Ecdysone receptor constrains wingless expression to pattern cell cycle across the Drosophila wing margin in a Cyclin B-dependent manner
- PMID: 23848468
- PMCID: PMC3720226
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-13-28
The Ecdysone receptor constrains wingless expression to pattern cell cycle across the Drosophila wing margin in a Cyclin B-dependent manner
Abstract
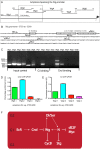
Background: Ecdysone triggers transcriptional changes via the ecdysone receptor (EcR) to coordinate developmental programs of apoptosis, cell cycle and differentiation. Data suggests EcR affects cell cycle gene expression indirectly and here we identify Wingless as an intermediary factor linking EcR to cell cycle.
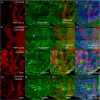
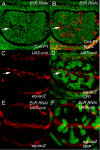
Results: We demonstrate EcR patterns cell cycle across the presumptive Drosophila wing margin by constraining wg transcription to modulate CycB expression, but not the previously identified Wg-targets dMyc or Stg. Furthermore co-knockdown of Wg restores CycB patterning in EcR knockdown clones. Wg is not a direct target of EcR, rather we demonstrate that repression of Wg by EcR is likely mediated by direct interaction between the EcR-responsive zinc finger transcription factor Crol and the wg promoter.
Conclusions: Thus we elucidate a critical mechanism potentially connecting ecdysone with patterning signals to ensure correct timing of cell cycle exit and differentiation during margin wing development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ecdysone receptor controls the post-critical weight switch to nutrition-independent differentiation in Drosophila wing imaginal discs.Development. 2009 Jul;136(14):2345-53. doi: 10.1242/dev.032672. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Development. 2009. PMID: 19515698 Free PMC article.
-
The Ecdysone-inducible zinc-finger transcription factor Crol regulates Wg transcription and cell cycle progression in Drosophila.Development. 2008 Aug;135(16):2707-16. doi: 10.1242/dev.021766. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Development. 2008. PMID: 18614577
-
Repression of dMyc expression by Wingless promotes Rbf-induced G1 arrest in the presumptive Drosophila wing margin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 16;101(11):3857-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400526101. Epub 2004 Mar 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15001704 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and widespread role for the nuclear receptor EcR in mediating the response to ecdysone in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 14;116(20):9893-9902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900343116. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31019084 Free PMC article.
-
The ecdysone regulatory pathway controls wing morphogenesis and integrin expression during Drosophila metamorphosis.Dev Biol. 2000 Apr 15;220(2):211-24. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9650. Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10753511
Cited by
-
Regulation of Body Size and Growth Control.Genetics. 2020 Oct;216(2):269-313. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303095. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 33023929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ecdysone receptor (EcR) is involved in the transcription of cell cycle genes in the silkworm.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Feb 3;16(2):3335-49. doi: 10.3390/ijms16023335. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25654229 Free PMC article.
-
BmFoxO Gene Regulation of the Cell Cycle Induced by 20-Hydroxyecdysone in BmN-SWU1 Cells.Insects. 2020 Oct 14;11(10):700. doi: 10.3390/insects11100700. Insects. 2020. PMID: 33066376 Free PMC article.
-
Ecdysone signaling induces two phases of cell cycle exit in Drosophila cells.Biol Open. 2016 Nov 15;5(11):1648-1661. doi: 10.1242/bio.017525. Biol Open. 2016. PMID: 27737823 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid hormone-induced wingless ligands tune female intestinal size in Drosophila.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 6;16(1):436. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55664-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39762218 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

