Hair loss and hair-pulling in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)
- PMID: 23849443
- PMCID: PMC3725930
Hair loss and hair-pulling in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta)
Abstract
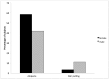
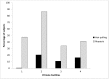
Alopecia is a common problem in rhesus macaque colonies. A possible cause of this condition is hair-pulling; however the true relationship between hair-pulling and alopecia is unknown. The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between hair loss and hair-pulling in 1258 rhesus macaques housed in 4 primate colonies across the United States. Alopecia levels ranged from 34.3% to 86.5% (mean, 49.3%) at the primate facilities. At facilities reporting a sex-associated difference, more female macaques were reported to exhibit alopecia than were males. In contrast, more males were reported to hair-pull. Animals reported to hair-pull were significantly more likely to have some amount of alopecia, but rates of hair-pulling were substantially lower than rates of alopecia, ranging from 0.6% to 20.5% (mean, 7.7%) of the populations. These results further demonstrate that hair-pulling plays only a small role in alopecia in rhesus macaques.
Figures
References
-
- Baker KC, Crockett CM, Bloomsmith MA, Coleman K, Bellanca RU. 2006. Behavioral and clinical management of alopecia in nonhuman primates. Am J Primatol 68 Suppl 1:89
-
- Baker KC, Weed JL, Crockett CM, Bloomsmith MA. 2007. Survey of environmental enhancement programs for laboratory primates. Am J Primatol 69:377–394 - PubMed
-
- Bayne K, Novak M. 1998. Behavioral disorders, p 485–500. In: Bennett BT, Abee CR, Henrickson R. Nonhuman primates in biomedical research diseases. New York (NY): Academic Press.
-
- Beisner BA, Isbell LA. 2008. Ground substrate affects activity budgets and hair loss in outdoor captive groups of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Am J Primatol 70:1160–1168 - PubMed
-
- Beisner BA, Isbell LA. 2009. Factors influencing hair loss among female captive rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Appl Anim Behav Sci 119:91–100
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources