CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes
- PMID: 23849981
- PMCID: PMC3770145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.044
CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes
Abstract
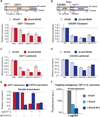
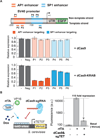
The genetic interrogation and reprogramming of cells requires methods for robust and precise targeting of genes for expression or repression. The CRISPR-associated catalytically inactive dCas9 protein offers a general platform for RNA-guided DNA targeting. Here, we show that fusion of dCas9 to effector domains with distinct regulatory functions enables stable and efficient transcriptional repression or activation in human and yeast cells, with the site of delivery determined solely by a coexpressed short guide (sg)RNA. Coupling of dCas9 to a transcriptional repressor domain can robustly silence expression of multiple endogenous genes. RNA-seq analysis indicates that CRISPR interference (CRISPRi)-mediated transcriptional repression is highly specific. Our results establish that the CRISPR system can be used as a modular and flexible DNA-binding platform for the recruitment of proteins to a target DNA sequence, revealing the potential of CRISPRi as a general tool for the precise regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Benoist C, Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981;290:304–310. - PubMed
-
- Bhaya D, Davison M, Barrangou R. CRISPR-Cas systems in bacteriaarchaea versatile small RNAs for adaptive defense and regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011;45:273–297. - PubMed
-
- Chang K, Elledge SJ, Hannon GJ. Lessons from Nature: microRNA-based shRNA libraries. Nat. Methods. 2006;3:707–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

