Menin: a scaffold protein that controls gene expression and cell signaling
- PMID: 23850066
- PMCID: PMC3741089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.05.005
Menin: a scaffold protein that controls gene expression and cell signaling
Abstract
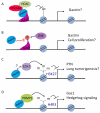
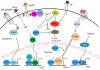
The protein menin is encoded by the MEN1 gene, which is mutated in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) syndrome. Although menin acts as a tumor suppressor in endocrine organs, it is required for leukemic transformation in mouse models. Menin possesses these dichotomous functions probably because it can both positively and negatively regulate gene expression, as well as interact with a multitude of proteins with diverse functions. Here, we review the recent progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms by which menin functions. The crystal structures of menin with different binding partners reveal that menin is a key scaffold protein that functionally crosstalks with various partners to regulate gene transcription and interplay with multiple signaling pathways.
Keywords: cell signaling; gene transcription; menin; scaffold protein.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Chandrasekharappa SC, et al. Positional cloning of the gene for multiple endocrine neoplasia-type 1. Science. 1997;276:404–407. - PubMed
-
- Lemmens I, et al. Identification of the multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) gene. The European Consortium on MEN1. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:1177–1183. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal SK, et al. Menin molecular interactions: insights into normal functions and tumorigenesis. Horm Metab Res. 2005;37:369–374. - PubMed
-
- Boikos SA, Stratakis CA. Molecular genetics of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathway and of sporadic pituitary tumorigenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16(Spec No 1):R80–87. - PubMed
-
- Lemos MC, Thakker RV. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1): analysis of 1336 mutations reported in the first decade following identification of the gene. Hum Mutat. 2008;29:22–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

