Chromatin-bound IκBα regulates a subset of polycomb target genes in differentiation and cancer
- PMID: 23850221
- PMCID: PMC3962677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.06.003
Chromatin-bound IκBα regulates a subset of polycomb target genes in differentiation and cancer
Abstract
IκB proteins are the primary inhibitors of NF-κB. Here, we demonstrate that sumoylated and phosphorylated IκBα accumulates in the nucleus of keratinocytes and interacts with histones H2A and H4 at the regulatory region of HOX and IRX genes. Chromatin-bound IκBα modulates Polycomb recruitment and imparts their competence to be activated by TNFα. Mutations in the Drosophila IκBα gene cactus enhance the homeotic phenotype of Polycomb mutants, which is not counteracted by mutations in dorsal/NF-κB. Oncogenic transformation of keratinocytes results in cytoplasmic IκBα translocation associated with a massive activation of Hox. Accumulation of cytoplasmic IκBα was found in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) associated with IKK activation and HOX upregulation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
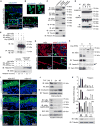
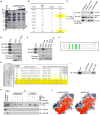

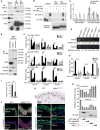
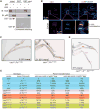

Comment in
-
Emerging from NF-κB's shadow, SUMOylated IκBα represses transcription.Cancer Cell. 2013 Aug 12;24(2):139-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.07.011. Cancer Cell. 2013. PMID: 23948292
References
-
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Turpin P, Rodriguez M, Thomas D, Hay RT, Virelizier JL, Dargemont C. Nuclear localization of I kappa B alpha promotes active transport of NF-kappa B from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:369–378. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988;242:540–546. - PubMed
-
- Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT, Baltimore D. Constitutive NF-kappa B activation, enhanced granulopoiesis, and neonatal lethality in I kappa B alpha-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2736–2746. - PubMed
-
- Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigó R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH, Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, Thurman RE, et al. ENCODE Project Consortium; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Baylor College of Medicine Human Genome Sequencing Center; Washington University Genome Sequencing Center; Broad Institute; Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 2007;447:799–816. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

