Sympathetic innervation during development is necessary for pancreatic islet architecture and functional maturation
- PMID: 23850289
- PMCID: PMC3740126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.019
Sympathetic innervation during development is necessary for pancreatic islet architecture and functional maturation
Abstract
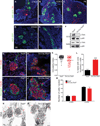
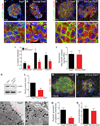
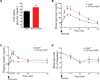
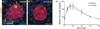
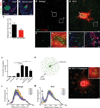
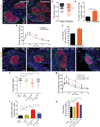
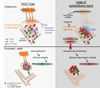
Sympathetic neurons depend on target-derived neurotrophic cues to control their survival and growth. However, whether sympathetic innervation contributes reciprocally to the development of target tissues is less clear. Here, we report that sympathetic innervation is necessary for the formation of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and for their functional maturation. Genetic or pharmacological ablation of sympathetic innervation during development resulted in altered islet architecture, reduced insulin secretion, and impaired glucose tolerance in mice. Similar defects were observed with pharmacological blockade of β-adrenergic signaling. Conversely, the administration of a β-adrenergic agonist restored islet morphology and glucose tolerance in deinnervated animals. Furthermore, in neuron-islet cocultures, sympathetic neurons promoted islet cell migration in a β-adrenergic-dependent manner. This study reveals that islet architecture requires extrinsic inductive cues from neighboring tissues such as sympathetic nerves and suggests that early perturbations in sympathetic innervation might underlie metabolic disorders.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ahren B. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion--implications for health and disease. Diabetologia. 2000;43:393–410. - PubMed
-
- Asensio C, Jimenez M, Kuhne F, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Muzzin P. The lack of beta-adrenoceptors results in enhanced insulin sensitivity in mice exhibiting increased adiposity and glucose intolerance. Diabetes. 2005;54:3490–3495. - PubMed
-
- Bonner-Weir S. Morphological evidence for pancreatic polarity of beta-cell within islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1988;37:616–621. - PubMed
-
- Bosco D, Orci L, Meda P. Homologous but not heterologous contact increases the insulin secretion of individual pancreatic B-cells. Experimental cell research. 1989;184:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Brissova M, Fowler MJ, Nicholson WE, Chu A, Hirshberg B, Harlan DM, Powers AC. Assessment of human pancreatic islet architecture and composition by laser scanning confocal microscopy. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society. 2005;53:1087–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

