The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor NVP-BKM120 overcomes resistance signals derived from microenvironment by regulating the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim axis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
- PMID: 23850807
- PMCID: PMC3815175
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.088849
The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor NVP-BKM120 overcomes resistance signals derived from microenvironment by regulating the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim axis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
Abstract
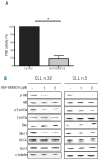
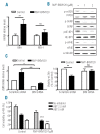
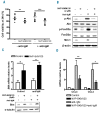
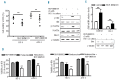
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway is constitutively activated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia mainly due to microenvironment signals, including stromal cell interaction and CXCR4 and B-cell receptor activation. Because of the importance of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, we investigated the activity of the NVP-BKM120, an orally available pan class I phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor. Sensitivity to NVP-BKM120 was analyzed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia primary samples in the context of B-cell receptor and microenvironment stimulation. NVP-BKM120 promoted mitochondrial apoptosis in most primary cells independently of common prognostic markers. NVP-BKM120 activity induced the blockage of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling, decreased Akt and FoxO3a phosphorylation leading to concomitant Mcl-1 downregulation and Bim induction. Accordingly, selective knockdown of BIM rescued cells from NVP-BKM120-induced apoptosis, while the kinase inhibitor synergistically enhanced the apoptosis induced by the BH3-mimetic ABT-263. We also found NVP-BKM120 to inhibit B-cell receptor- and stroma-dependent Akt pathway activation, thus sensitizing chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to bendamustine and fludarabine. Furthermore, NVP-BKM120 down-regulated secretion of chemokines after B-cell receptor stimulation and inhibited cell chemotaxis and actin polymerization upon CXCR4 triggering by CXCL12. Our findings establish that NVP-BKM120 effectively inhibits the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling pathway and disturbs the protective effect of the tumor microenvironment with the subsequent apoptosis induction through the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim axis. We provide here a strong rationale for undertaking clinical trials of NVP-BKM120 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients alone or in combination therapies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling by NVP-BKM120 promotes ABT-737-induced toxicity in a caspase-dependent manner through mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage response in established and primary cultured glioblastoma cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Jul;350(1):22-35. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.212910. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24741074 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of NVP-BKM120--a selective pan class I PI3 kinase inhibitor showed differential forms of cell death based on p53 status of glioma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;18(1):184-95. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1558. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22065080 Free PMC article.
-
ERK-dependent IL-6 autocrine signaling mediates adaptive resistance to pan-PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 18;37(3):377-388. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.339. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28945228
-
The role of B-cell receptor inhibitors in the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Haematologica. 2015 Dec;100(12):1495-507. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.119123. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 26628631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of FOXO3 Activated by HIV-1 Tat in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder Neuronal Apoptosis.Front Neurosci. 2019 Feb 4;13:44. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00044. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30778283 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl(Suppl):S25-S54. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25892662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isotype-specific inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway in hematologic malignancies.Onco Targets Ther. 2014 Feb 21;7:333-42. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S34641. eCollection 2014. Onco Targets Ther. 2014. PMID: 24591840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adverse events in lymphoma patients treated with phosphoinositide 3 kinase Inhibitor in clinical trials: a meta-analysis.Ann Hematol. 2022 Aug;101(8):1741-1753. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-04876-x. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Ann Hematol. 2022. PMID: 35688904
-
Effects of PI3K inhibitor NVP-BKM120 on overcoming drug resistance and eliminating cancer stem cells in human breast cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Dec 17;6(12):e2020. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.363. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26673665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burger JA. Targeting the microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is changing the therapeutic landscape. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012;24(6):643–9 - PubMed
-
- Ringshausen I, Schneller F, Bogner C, Hipp S, Duyster J, Peschel C, et al. Constitutively activated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) is involved in the defect of apoptosis in B-CLL: association with protein kinase Cdelta. Blood. 2002;100(10):3741–8 - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(5):329–41 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

