Membrane trafficking of death receptors: implications on signalling
- PMID: 23852022
- PMCID: PMC3742255
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140714475
Membrane trafficking of death receptors: implications on signalling
Abstract
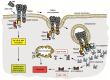
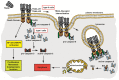
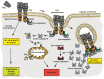
Death receptors were initially recognised as potent inducers of apoptotic cell death and soon ambitious attempts were made to exploit selective ignition of controlled cellular suicide as therapeutic strategy in malignant diseases. However, the complexity of death receptor signalling has increased substantially during recent years. Beyond activation of the apoptotic cascade, involvement in a variety of cellular processes including inflammation, proliferation and immune response was recognised. Mechanistically, these findings raised the question how multipurpose receptors can ensure selective activation of a particular pathway. A growing body of evidence points to an elegant spatiotemporal regulation of composition and assembly of the receptor-associated signalling complex. Upon ligand binding, receptor recruitment in specialized membrane compartments, formation of receptor-ligand clusters and internalisation processes constitute key regulatory elements. In this review, we will summarise the current concepts of death receptor trafficking and its implications on receptor-associated signalling events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human astrocytes are resistant to Fas ligand and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 22;26(12):3299-308. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5572-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16554480 Free PMC article.
-
Life and death by death receptors.FASEB J. 2009 Jun;23(6):1625-37. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-111005. Epub 2009 Jan 13. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19141537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Death receptors.Essays Biochem. 2003;39:53-71. doi: 10.1042/bse0390053. Essays Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14585074 Review.
-
Structural determinants of DISC function: new insights into death receptor-mediated apoptosis signalling.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;140(2):186-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23845861 Review.
-
Surfactant protein D delays Fas- and TRAIL-mediated extrinsic pathway of apoptosis in T cells.Apoptosis. 2017 May;22(5):730-740. doi: 10.1007/s10495-017-1348-4. Apoptosis. 2017. PMID: 28168327
Cited by
-
CD4+ T cells apoptosis in Plasmodium vivax infection is mediated by activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.Malar J. 2015 Jan 5;14:5. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-14-5. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 25559491 Free PMC article.
-
Death Receptors DR4 and DR5 Undergo Spontaneous and Ligand-Mediated Endocytosis and Recycling Regardless of the Sensitivity of Cancer Cells to TRAIL.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 30;9:733688. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.733688. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34660590 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity of TNF-α Signaling in Heart Disease.J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 12;9(10):3267. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103267. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33053859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Central Nervous System Contains ILC1s That Differ From NK Cells in the Response to Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 10;10:2337. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02337. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31649664 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical Studies on the Engagement of Interleukin 18 in the Immuno-Inflammatory Processes Underlying Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 5;19(11):3476. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113476. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30400655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodmer J.L., Schneider P., Tschopp J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Ware C.F. The TNF superfamily. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:181–184. - PubMed
-
- Wiens G.D., Glenney G.W. Origin and evolution of TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011;35:1324–1335. - PubMed
-
- Locksley R.M., Killeen N., Lenardo M.J. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources