Canceling actions involves a race between basal ganglia pathways
- PMID: 23852117
- PMCID: PMC3733500
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3456
Canceling actions involves a race between basal ganglia pathways
Abstract
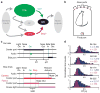
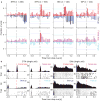
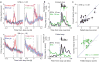
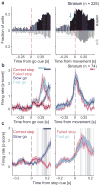
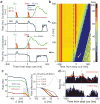
Salient cues can prompt the rapid interruption of planned actions. It has been proposed that fast, reactive behavioral inhibition involves specific basal ganglia pathways, and we tested this by comparing activity in multiple rat basal ganglia structures during performance of a stop-signal task. Subthalamic nucleus (STN) neurons exhibited low-latency responses to 'Stop' cues, irrespective of whether actions were canceled or not. By contrast, neurons downstream in the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) only responded to Stop cues in trials with successful cancellation. Recordings and simulations together indicate that this sensorimotor gating arises from the relative timing of two distinct inputs to neurons in the SNr dorsolateral 'core' subregion: cue-related excitation from STN and movement-related inhibition from striatum. Our results support race models of action cancellation, with stopping requiring Stop-cue information to be transmitted from STN to SNr before increased striatal input creates a point of no return.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
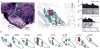
Comment in
-
Motor control: A race to the (s)top.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Sep;14(9):590-1. doi: 10.1038/nrn3569. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23900410 No abstract available.
-
Subthalamic nucleus and striatum: the red and green signals to regulate the traffic of basal ganglia circuitry.Mov Disord. 2013 Nov;28(13):1802. doi: 10.1002/mds.25694. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 24151032 No abstract available.
References
-
- Logan GD, Cowan WB, Davis KA. On the ability to inhibit simple and choice reaction time responses: a model and a method. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 1984;10:276–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

