Antiretroviral therapy initiated within 6 months of HIV infection is associated with lower T-cell activation and smaller HIV reservoir size
- PMID: 23852127
- PMCID: PMC3778965
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jit311
Antiretroviral therapy initiated within 6 months of HIV infection is associated with lower T-cell activation and smaller HIV reservoir size
Abstract
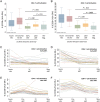
Background. CD4(+)/CD8(+) T-cell activation levels often remain elevated in chronic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection despite initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART). T-cell activation predicts early death and blunted CD4+ T-cell recovery during ART and may affect persistent HIV reservoir size. We investigated whether very early ART initiation is associated with lower on-therapy immune activation and HIV persistence. Methods. From a cohort of patients with early HIV infection (<6 months duration since infection) we identified persons who started ART early (<6 months after infection) or later (≥2 years after infection) and maintained ≥2 years of virologic suppression; at-risk HIV-negative persons were controls. We measured CD4(+)/CD8(+) T-cell activation (percent CD38(+)/HLA-DR(+)) and HIV reservoir size (based on HIV DNA and cell-associated RNA levels). Results. In unadjusted analyses, early ART predicted lower on-therapy CD8(+) T-cell activation (n = 34; mean, 22.1%) than achieved with later ART (n = 32; mean, 28.8%; P = .009), although levels in early ART remained elevated relative to HIV-negative controls (P = .02). Early ART also predicted lower CD4+ T-cell activation than with later ART (5.3% vs 7.5%; P = .06). Early ART predicted 4.8-fold lower DNA levels than achieved with later ART (P = .005), and lower cell-associated RNA levels (difference in signal-to-cutoff ratio (S/Co), 3.2; P = .035). Conclusions. ART initiation <6 months after infection is associated with lower levels of T-cell activation and smaller HIV DNA and RNA reservoir size during long-term therapy.
Keywords: HIV antiretroviral therapy; HIV cure; HIV eradication; HIVreservoir; T-cell activation; early ART; inflammation.
Figures

Comment in
-
Early treatment and HIV-1 reservoirs: a stitch in time?J Infect Dis. 2013 Oct 15;208(8):1189-93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit307. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23852126 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bofill M, Mocroft A, Lipman M, et al. Increased numbers of primed activated CD8+CD38+CD45RO+ T cells predict the decline of CD4+ T cells in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS. 1996;10:827–34. - PubMed
-
- Giorgi JV, Hultin LE, McKeating JA, et al. Shorter survival in advanced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection is more closely associated with T lymphocyte activation than with plasma virus burden or virus chemokine coreceptor usage. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:859–70. - PubMed
-
- Hunt PW, Martin JN, Sinclair E, et al. T cell activation is associated with lower CD4+ T cell gains in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with sustained viral suppression during antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:1534–43. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi RT, Spritzler J, Chan E, et al. Effect of baseline- and treatment-related factors on immunologic recovery after initiation of antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-positive subjects: results from ACTG 384. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006;42:426–34. - PubMed
-
- Goicoechea M, Smith DM, Liu L, et al. Determinants of CD4+ T cell recovery during suppressive antiretroviral therapy: association of immune activation, T cell maturation markers, and cellular HIV-1 DNA. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:29–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

