The therapeutic potential of GPR43: a novel role in modulating metabolic health
- PMID: 23852543
- PMCID: PMC11113592
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-013-1419-9
The therapeutic potential of GPR43: a novel role in modulating metabolic health
Abstract
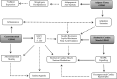
GPR43 is a receptor for short-chain fatty acids. Preliminary data suggest a putative role for GPR43 in regulating systemic health via processes including inflammation, carcinogenesis, gastrointestinal function, and adipogenesis. GPR43 is involved in secretion of gastrointestinal peptides, which regulate appetite and gastrointestinal motility. This suggests GPR43 may have a role in weight control. Moreover, GPR43 regulates plasma lipid profile and inflammatory processes, which further indicates that GPR43 could have the ability to modulate the etiology and pathogenesis of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease. This review summarizes the current evidence regarding the ability of GPR43 to mediate both systemic and tissue specific functions and how GPR43 may be modulated in the treatment of metabolic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lundstrom K. Latest development in drug discovery on G protein-coupled receptors. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2006;7(5):465–470. - PubMed
-
- Le Poul E, et al. Functional characterization of human receptors for short-chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(28):25481–25489. - PubMed
-
- Brown AJ, et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short-chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(13):11312–11319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

