Quantification of adipose tissue leukocytosis in obesity
- PMID: 23852606
- PMCID: PMC3972009
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-523-1_15
Quantification of adipose tissue leukocytosis in obesity
Abstract
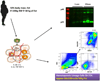
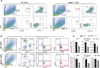
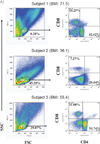
The infiltration of immune cell subsets in adipose tissue termed "adipose tissue leukocytosis" is a critical event in the development of chronic inflammation and obesity-associated comorbidities. Given that a significant proportion of cells in adipose tissue of obese patients are of hematopoietic lineage, the distinct adipose depots represent an uncharacterized immunological organ that can impact metabolic functions. Here, we describe approaches to characterize and isolate leukocytes from the complex adipose tissue microenvironment, to aid mechanistic studies to better understand the role of specific pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as inflammasomes in adipose-immune cross talk.
Figures



References
-
- Greenberg AS, Obin MS. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2006;83(2):461S–465S. - PubMed
-
- Winer DA, Winer S, Shen L, Wadia PP, Yantha J, Paltser G, Tsui H, Wu P, Davidson MG, Alonso MN, Leong HX, Glassford A, Caimol M, Kenkel JA, Tedder TF, McLaughlin T, Miklos DB, Dosch HM, Engleman EG. B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nature medicine. 2011;17(5):610–617. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rausch ME, Weisberg S, Vardhana P, Tortoriello DV. Obesity in C57BL/6J mice is characterized by adipose tissue hypoxia and cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32(3):451–463. - PubMed
-
- Elgazar-Carmon V, Rudich A, Hadad N, Levy R. Neutrophils transiently infiltrate intra-abdominal fat early in the course of high-fat feeding. Journal of lipid research. 2008;49(9):1894–1903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

