Preventive Effects of a Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agent, Astragaloside IV, on Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury in Rats
- PMID: 23853656
- PMCID: PMC3703719
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/284025
Preventive Effects of a Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agent, Astragaloside IV, on Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury in Rats
Abstract
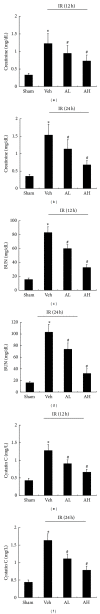
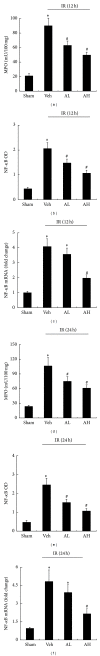
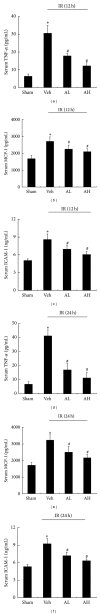
This study investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of astragaloside IV(AS-IV) on ischemia/reperfusion (IR) induced acute kidney injury (AKI) in rats. Experimental model of ischemic AKI was induced in rats by bilateral renal artery clamp for 45 min followed by reperfusion of 12 h and 24 h, respectively. AS-IV was orally administered once a day to rats at 10 and 20 mg·kg(-1)·d(-1) for 7 days prior to ischemia. AS-IV pretreatment significantly decreased serum urea, creatinine, and cystatin C levels at 12 h and 24 h of reperfusion in AKI rats. AS-IV pretreatment also ameliorated tubular damage and suppressed the phosphorylation of p65 subunit of NF- κ B in AKI rats. Moreover, NF- κ B and MPO activity as well as serum and tissue levels of TNF- α , MCP-1, and ICAM-1 were elevated in AKI rats. All of these abnormalities were prevented by AS-IV. Furthermore, AS-IV downregulated the mRNA expression of NF- κ B, TNF- α , MCP-1, and ICAM-1 in AKI rats. These results suggest that AS-IV might be developed as a novel therapeutic approach to prevent ischemic AKI through inhibition of NF- κ B mediated inflammatory genes expression.
Figures




References
-
- Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI. The effect of acute renal failure on mortality: a cohort analysis. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1996;275(19):1489–1494. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2005;16(11):3365–3370. - PubMed
-
- Schiffl H, Lang SM, Fischer R. Daily hemodialysis and the outcome of acute renal failure. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;346(5):305–310. - PubMed
-
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1996;334(22):1448–1460. - PubMed
-
- Rabb H, O’Meara YM, Maderna P, Coleman P, Brady HR. Leukocytes, cell adhesion molecules and ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney International. 1997;51(5):1463–1468. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

