Randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial of gabapentin during an outpatient, buprenorphine-assisted detoxification procedure
- PMID: 23855333
- PMCID: PMC3972066
- DOI: 10.1037/a0033724
Randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial of gabapentin during an outpatient, buprenorphine-assisted detoxification procedure
Abstract
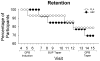
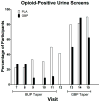
This pilot study examined the efficacy of the N-type calcium channel blocker gabapentin to improve outcomes during a brief detoxification protocol with buprenorphine. Treatment-seeking opioid-dependent individuals were enrolled in a 5-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial examining the effects of gabapentin during a 10-day outpatient detoxification from buprenorphine. Participants were inducted onto buprenorphine sublingual tablets during Week 1, were randomized and inducted onto gabapentin or placebo during Week 2, underwent a 10-day buprenorphine taper during Weeks 3 and 4, and then were tapered off gabapentin/placebo during Week 5. Assessments included thrice-weekly opioid withdrawal scales, vitals, and urine drug screens. Twenty-four individuals (13 male; 17 Caucasian, 3 African American, 4 Latino; mean age 29.7 years) participated in the detoxification portion of the study (gabapentin, n = 11; placebo, n = 13). Baseline characteristics did not differ significantly between groups. Self-reported and observer-rated opioid withdrawal ratings were relatively low and did not differ between groups during the buprenorphine taper. Urine results showed a Drug × Time interaction, such that the probability of opioid-positive urines significantly decreased over time in the gabapentin versus placebo groups during Weeks 3 and 4 (OR = 0.73, p = .004). These results suggest that gabapentin reduces opioid use during a 10-day buprenorphine detoxification procedure.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2013 APA, all rights reserved
Figures


References
-
- Amato L, Davoli M, Minozzi S, Ali R, Ferri M. Methadone at tapered doses for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Systematic Reviews. 2005;(3):CD003409. - PubMed
-
- Andrews N, Loomis S, Blake R, Ferrigan L, Singh L, McKnight AT. Effect of gabapentin-like compounds on development and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Psychopharmacology. 2001;157(4):381–387. - PubMed
-
- Barrios M, Baeyens JM. Differential effects of L-type calcium channel blockers and stimulants on naloxone-precipitated withdrawal in mice acutely dependent on morphine. Psychopharmacology. 1991;104(3):397–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

