Body composition assessment in overweight women: validation of air displacement plethysmography
- PMID: 23855413
- PMCID: PMC4361892
- DOI: 10.1111/cpf.12067
Body composition assessment in overweight women: validation of air displacement plethysmography
Abstract
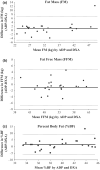
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the validity and reliability of air displacement plethysmography (ADP) compared to a dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) criterion for body composition measurement in overweight and obese women (BMI ≥ 25·0 kg m(2) ).
Subjects/methods: Twenty-four overweight and obese women (Mean ± SD; Age: 36·6 ± 12·0 years; Height: 166·4 ± 5·8 cm; Weight: 86·5 ± 14·2 kg; Body Fat: 38·5 ± 3·7%; BMI: 31·3 ± 5·5 kg m(2) ) were tested after an 8-h fast. Fat mass (FM), fat-free mass (FFM) and percent body fat (%BF) were measured by ADP and compared to values determined by the DXA criterion. FFM from DXA was calculated as lean mass plus bone mineral content. A paired samples t-test was used to test for significant differences in the body composition variables between methods. A one-way ANOVA along with intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), SEM,%SEM and MD was used to represent reliability.
Results: Validity data comparing ADP and DXA demonstrated no significant difference in FM (ADP-DXA FM = 0·99 kg; P = 0·113), FFM (0·98 kg; P = 0·115) and %BF (1·56%; P = 0·540). Reliability data for ADP between the first and second trials showed no significant difference in FM (P = 0·168; ICC = 0·994; SEM = 0·668), FFM (P = 0·058; ICC = 0·973; SEM = 0·892) or %BF (P = 0·121; ICC = 0·971; SEM = 0·813).
Conclusions: For overweight and obese women, ADP was found to be a valid measure of FM, FFM and %BF when compared with DXA. The reliability of ADP was supported for all body composition variables.
Keywords: dual energy x-ray absorptiometry; fat-free mass; percent body fat; sensitivity; sex.
© 2013 Scandinavian Society of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in thoracic gas volume with air-displacement plethysmography after a weight loss program in overweight and obese women.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008 Mar;62(3):444-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602709. Epub 2007 Mar 28. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008. PMID: 17392701
-
Body composition analysis by air displacement plethysmography in normal weight to extremely obese adults.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Apr;22(4):1078-84. doi: 10.1002/oby.20655. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 24170704 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in body composition measurements assessed by air displacement plethysmography and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in young and middle-aged adults.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2022 Aug;50:111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.06.014. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2022. PMID: 35871911
-
Body composition in preterm infants: a systematic review on measurement methods.Pediatr Res. 2023 Apr;93(5):1120-1140. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02262-x. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 35995939
-
Validity of multi-frequency bioelectric impedance methods to measure body composition in obese patients: a systematic review.Int J Obes (Lond). 2019 Aug;43(8):1497-1507. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0285-9. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30568268
Cited by
-
Validity of Body-Composition Methods across Racial and Ethnic Populations.Adv Nutr. 2021 Oct 1;12(5):1854-1862. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab016. Adv Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33684215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Preventiometer - reliability of a cardiovascular multi-device measurement platform and its measurement agreement with a cohort study.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Apr 24;23(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-01911-x. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023. PMID: 37095457 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and reliability of total body volume and relative body fat mass from a 3-dimensional photonic body surface scanner.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 3;12(7):e0180201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180201. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28672039 Free PMC article.
-
A new anthropometric index for body fat estimation in patients with severe obesity.BMC Obes. 2018 Oct 1;5:25. doi: 10.1186/s40608-018-0202-8. eCollection 2018. BMC Obes. 2018. PMID: 30288293 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Technologies and their Applications in Lipid Compartment Measurement.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec;26(12):688-698. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26596676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson DE. Reliability of air displacement plethysmography. J Strength Cond Res. 2007;21:169–172. - PubMed
-
- Bertoli S, Battezzati A, Testolin G, Bedogni G. Evaluation of air-displacement plethysmography and bioelectrical impedance analysis vs dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of fat-free mass in elderly subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008;62:1282–1286. - PubMed
-
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Brozek J, Grande F, Anderson JT, Keys A. Densitometric analysis of body composition: revision of some quantitative assumptions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963;110:113–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

