The importance of hydrogen bonding and aromatic stacking to the affinity and efficacy of cannabinoid receptor CB2 antagonist, 5-(4-chloro-3-methylphenyl)-1-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-N-[(1S,2S,4R)-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl]-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide (SR144528)
- PMID: 23855811
- PMCID: PMC3804063
- DOI: 10.1021/jm400070u
The importance of hydrogen bonding and aromatic stacking to the affinity and efficacy of cannabinoid receptor CB2 antagonist, 5-(4-chloro-3-methylphenyl)-1-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-N-[(1S,2S,4R)-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl]-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide (SR144528)
Abstract
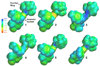
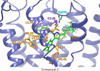
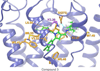
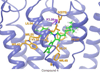
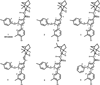
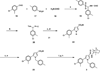
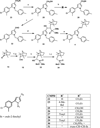
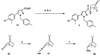
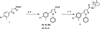
Despite the therapeutic promise of the subnanomolar affinity cannabinoid CB2 antagonist, 5-(4-chloro-3-methylphenyl)-1-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-N-[(1S,2S,4R)-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl]-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide (SR144528, 1), little is known about its binding site interactions and no primary interaction site for 1 at CB2 has been identified. We report here the results of Glide docking studies in our cannabinoid CB2 inactive state model that were then tested via compound synthesis, binding, and functional assays. Our results show that the amide functional group of 1 is critical to its CB2 affinity and efficacy and that aromatic stacking interactions in the TMH5/6 aromatic cluster of CB2 are also important. Molecular modifications that increased the positive electrostatic potential in the region between the fenchyl and aromatic rings led to more efficacious compounds. This result is consistent with the EC-3 loop negatively charged amino acid, D275 (identified via Glide docking studies) acting as the primary interaction site for 1 and its analogues.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tricyclic Pyrazole-Based Compounds as Useful Scaffolds for Cannabinoid CB1/CB2 Receptor Interaction.Molecules. 2021 Apr 7;26(8):2126. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082126. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33917187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in cannabinoid 1 vs. cannabinoid 2 receptor-selective antagonism of antinociception produced by delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and CP55,940 in the rat.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Mar;340(3):787-800. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.188540. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22182934
-
Evaluation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor-selective antagonist, SR144528: further evidence for cannabinoid CB2 receptor absence in the rat central nervous system.Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Jul 14;377(1):117-25. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00402-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10448934
-
Functional Selectivity of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands at a Canonical and Noncanonical Pathway.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Aug;358(2):342-51. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.232561. Epub 2016 May 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 27194477 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, pharmacological evaluation and docking studies of pyrrole structure-based CB2 receptor antagonists.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Aug 28;101:651-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.06.057. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26209834
Cited by
-
Discovery of Potent and Selective CB2 Agonists Utilizing a Function-Based Computational Screening Protocol.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Nov 1;14(21):3941-3958. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00580. Epub 2023 Oct 12. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37823773 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonization of OX1 Receptor Potentiates CB2 Receptor Function in Microglia from APPSw/Ind Mice Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;23(21):12801. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112801. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361598 Free PMC article.
-
Aromatic interactions at the ligand-protein interface: Implications for the development of docking scoring functions.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018 Feb;91(2):380-390. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13084. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018. PMID: 28816025 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: From the bench, toward the clinic: therapeutic opportunities for cannabinoid receptor modulation.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;29(6):801-13. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1062. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25866875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tricyclic Pyrazole-Based Compounds as Useful Scaffolds for Cannabinoid CB1/CB2 Receptor Interaction.Molecules. 2021 Apr 7;26(8):2126. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082126. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33917187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Galiegue S, Mary S, Marchand J, Dussossoy D, Carriere D, Carayon P, Bouaboula M, Shire D, Le Fur G, Casellas P. Expression of central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors in human immune tissues and leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Biochem. 1995;232:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, Felder CC, Herkenham M, Mackie K, Martin BR, Mechoulam R, Pertwee RG. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:161–202. - PubMed
-
- Van Sickle MD, Duncan M, Kingsley PJ, Mouihate A, Urbani P, Mackie K, Stella N, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D, Davison JS, Marnett LJ, Di Marzo V, Pittman QJ, Patel KD, Sharkey KA. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science. 2005;310:329–332. - PubMed
-
- Buckley NE, McCoy KL, Mezey E, Bonner T, Zimmer A, Felder CC, Glass M. Immunomodulation by cannabinoids is absent in mice deficient for the cannabinoid CB(2) receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;396:141–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

