Long-term risk of acute diverticulitis among patients with incidental diverticulosis found during colonoscopy
- PMID: 23856358
- PMCID: PMC5731451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.020
Long-term risk of acute diverticulitis among patients with incidental diverticulosis found during colonoscopy
Abstract
Background & aims: Colonic diverticulosis is the most common finding during routine colonoscopy, and patients often question the significance of these lesions. Guidelines state that these patients have a 10% to 25% lifetime risk of developing acute diverticulitis. However, this value was determined based on limited data, collected before population-based colonoscopy, so the true number of cases of diverticulosis was not known. We measured the long-term risk of acute diverticulitis among patients with confirmed diverticulosis discovered incidentally on colonoscopy.
Methods: We performed a retrospective study using administrative and clinical data from the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, collecting data on patients who underwent colonoscopies from January 1996 through January 2011. We identified patients diagnosed with diverticulosis, determined incidence rates per 1000 patient-years, and analyzed a subgroup of patients with rigorously defined events confirmed by imaging or surgery. We used a Cox proportional hazards model to identify factors associated with the development of diverticulitis.
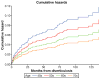
Results: We identified 2222 patients with baseline diverticulosis. Over an 11-year follow-up period, 95 patients developed diverticulitis (4.3%; 6 per 1000 patient-years); of these, 23 met the rigorous definition of diverticulitis (1%; 1.5 per 1000 patient-years). The median time-to-event was 7.1 years. Each additional decade of age at time of diagnosis reduced the risk for diverticulitis by 24% (hazard ratio, 0.76; 95% confidence interval, 0.6-0.9).
Conclusions: Based on a study of the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, only about 4% of patients with diverticulosis develop acute diverticulitis, contradicting the common belief that diverticulosis has a high rate of progression. We also found that younger patients have a higher risk of diverticulitis, with risk increasing per year of life. These results can help inform patients with diverticulosis about their risk of developing acute diverticulitis.
Keywords: BMI; CT; Colon; Diverticular Disease; ICD-9; International Classification of Diseases, 9th revision; Pouch; Prognosis; VA; VAGLAHS; Veteran's Affairs; Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System; body mass index; computed tomography.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
These authors disclose the following: Brennan Spiegel has served as an advisor for Ironwood Pharmaceuticals and has received research support from Amgen, Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, and Shire Pharmaceuticals; and Linnette Yen, Paul Hodgkins, and M. Haim Erder are employees of Shire Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is there really anything new on dietary fiber in colonic diverticular disease?Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Jul;12(7):1200-1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.01.015. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24440219 No abstract available.
References
-
- Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States part II: lower gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:741–754. - PubMed
-
- Shaheen NJ, Hansen RA, Morgan DR, et al. The burden of gastrointestinal and liver diseases, 2006. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:2128–2138. - PubMed
-
- Delvaux M. Diverticular disease of the colon in Europe: epidemiology, impact on citizen health and prevention. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18(Suppl 3):71–74. - PubMed
-
- Parks TG. Natural history of diverticular disease of the colon. Clin Gastroenterol. 1975;4:53–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous