Interleukin-6 limits influenza-induced inflammation and protects against fatal lung pathology
- PMID: 23857287
- PMCID: PMC3886386
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201243018
Interleukin-6 limits influenza-induced inflammation and protects against fatal lung pathology
Abstract
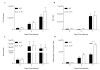
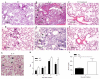
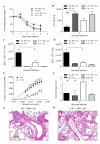
Balancing the generation of immune responses capable of controlling virus replication with those causing immunopathology is critical for the survival of the host and resolution of influenza-induced inflammation. Based on the capacity of interleukin-6 (IL-6) to govern both optimal T-cell responses and inflammatory resolution, we hypothesised that IL-6 plays an important role in maintaining this balance. Comparison of innate and adaptive immune responses in influenza-infected wild-type control and IL-6-deficient mice revealed striking differences in virus clearance, lung immunopathology and generation of heterosubtypic immunity. Mice lacking IL-6 displayed a profound defect in their ability to mount an anti-viral T-cell response. Failure to adequately control virus was further associated with an enhanced infiltration of inflammatory monocytes into the lung and an elevated production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, IFN-α and TNF-α. These events were associated with severe lung damage, characterised by profound vascular leakage and death. Our data highlight an essential role for IL-6 in orchestrating anti-viral immunity through an ability to limit inflammation, promote protective adaptive immune responses and prevent fatal immunopathology.
Keywords: Adaptive immunity · Heterosubtypic immunity · IL-6 · Innate immunity · Pulmonary damage.
© 2013 Cardiff University. European Journal of Immunology published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures





References
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD, Chin B, Feehan D, Hill KH. Estimation of potential global pandemic influenza mortality on the basis of vital registry data from the 1918-20 pandemic: a quantitative analysis. Lancet. 2006;368:2211–2218. - PubMed
-
- Yuen KY, Chan PK, Peiris M, Tsang DN, Que TL, Shortridge KF, Cheung PT, et al. Clinical features and rapid viral diagnosis of human disease associated with avian influenza A H5N1 virus. Lancet. 1998;351:467–471. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser L, Fritz RS, Straus SE, Gubareva L, Hayden FG. Symptom pathogenesis during acute influenza: interleukin-6 and other cytokine responses. J Med Virol. 2001;64:262–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

