Postpartum misoprostol for preventing maternal mortality and morbidity
- PMID: 23857523
- PMCID: PMC11878482
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008982.pub2
Postpartum misoprostol for preventing maternal mortality and morbidity
Abstract
Background: The primary objective of postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) prevention and treatment is to reduce maternal deaths. Misoprostol has the major public health advantage over injectable medication that it can more easily be distributed at community level. Because misoprostol might have adverse effects unrelated to blood loss which might impact on mortality or severe morbidity, it is important to continue surveillance of all relevant evidence from randomised trials. This is particularly important as misoprostol is being introduced on a large scale for PPH prevention in low-income countries, and is commonly used for PPH treatment in well-resourced settings as well.
Objectives: To review maternal deaths and severe morbidity in all randomised trials of misoprostol for prevention or treatment of PPH.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group's Trials Register (11 January 2013).
Selection criteria: We included randomised trials including pregnant women who received misoprostol in the postpartum period, versus placebo/no treatment or other uterotonics for prevention or treatment of PPH, and reporting on maternal death, severe morbidity or pyrexia.We planned to include cluster- and quasi-randomised trials in the analysis, as a very large number of women will be needed to obtain robust estimates of maternal mortality but we did not identify any for this version of the review. In future updates of this review we will include trials reported only as abstracts if sufficient information is available from the abstract or from the authors.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trials for inclusion and extracted data.
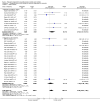
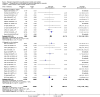
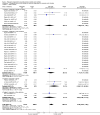
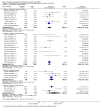
Main results: We included 78 studies (59,216 women) and excluded 34 studies.There was no statistically significant difference in maternal mortality for misoprostol compared with control groups overall (31 studies; 11/19,715 versus 4/20,076 deaths; risk ratio (RR) 2.08, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.82 to 5.28); or for the trials of misoprostol versus placebo: 10 studies, 6/4626 versus 1/4707 ; RR 2.70; 95% CI 0.72 to 10.11; or for misoprostol versus other uterotonics: 21 studies, 5/15,089 versus 3/15,369 (19/100,000); RR 1.54; 95% CI 0.40 to 5.92. All 11 deaths in the misoprostol arms occurred in studies of misoprostol ≥ 600 µg.There was a statistically significant difference in the composite outcome 'maternal death or severe morbidity' for the comparison of misoprostol versus placebo (12 studies; average RR 1.70, 95% CI 1.02 to 2.81; Tau² = 0.00, I² = 0%) but not for the comparison of misoprostol versus other uterotonics (17 studies; average RR 1.50, 95% CI 0.50 to 4.52; Tau² = 1.81, I² = 69%). When we excluded hyperpyrexia from the composite outcome in exploratory analyses, there was no significant difference in either of these comparisons.Pyrexia > 38°C was increased with misoprostol compared with controls (56 studies, 2776/25,647 (10.8%) versus 614/26,800 (2.3%); average RR 3.97, 95% CI 3.13 to 5.04; Tau² = 0.47, I² = 80%). The effect was greater for trials using misoprostol 600 µg or more (27 studies; 2197/17,864 (12.3%) versus 422/18,161 (2.3%); average RR 4.64; 95% CI 3.33 to 6.46; Tau² = 0.51, I² = 86%) than for those using misoprostol 400 µg or less (31 studies; 525/6751 (7.8%) versus 185/7668 (2.4%); average RR 3.07; 95% CI 2.25 to 4.18; Tau² = 0.29, I² = 58%).
Authors' conclusions: Misoprostol does not appear to increase or reduce severe morbidity (excluding hyperpyrexia) when used to prevent or treat PPH. Misoprostol did not increase or decrease maternal mortality. However, misoprostol is associated with an increased risk of pyrexia, particularly in dosages of 600 µg or more. Given that misoprostol is used prophylactically in very large numbers of healthy women, the greatest emphasis should be placed on limiting adverse effects. In this context, the findings of this review support the use of the lowest effective dose. As for any new medication being used on a large scale, continued vigilance for adverse effects is essential and there is a need for large randomised trials to further elucidate both the relative effectiveness and the risks of various dosages of misoprostol.
Conflict of interest statement
GJH and AMG have participated in trials eligible for consideration of inclusion in the review. They did not participate in decisions regarding such trials. GJH has received research funding from Gynuity, a non‐profit organisation, for conducting a trial of misoprostol for preventing postpartum haemorrhage.
Figures







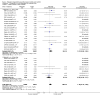
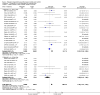



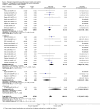
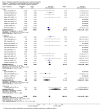
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Australia 1999:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Cook CM, Spurrett B, Murray H. A randomized clinical trial comparing oral misoprostol with synthetic oxytocin or syntometrine in the third stage of labour. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1999;39(4):414‐9. - PubMed
Bangla 2007:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Sultana N, Khatun M. Misoprostol versus oxytocin in the active management of the third stage of labour. Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons 2007;25(2):73‐6.
Belgium 1999:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Amant F, Spitz B, Timmerman D, Corresmans A, Assche FA. Misoprostol compared with methylergometrine for the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage: a double‐blind randomised trial. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1999;106:1066‐70. - PubMed
BETV 2010:800SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Blum J, Winikoff B, Raghavan S, Dabash R, Ramadan MC, Dilbaz B, et al. Treatment of post‐partum haemorrhage with sublingual misoprostol versus oxytocin in women receiving prophylactic oxytocin: a double‐blind, randomised, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet 2010;375(9710):217‐23. - PubMed
-
- Blum J, Winikoff B, Raghavan S, Dabash R, Ramadan MC, Dilbaz B, et al. Treatment of postpartum hemorrhage with sublingual misoprostol versus oxytocin: results from a randomized non‐inferiority trial among women receiving prophylactic oxytocin. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S22‐3.
-
- Dao B, Blum J, Barrera G, Cherine Ramadan M, Dabash R, Darwish E, et al. Side effect profiles for misoprostol and oxytocin in the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S150.
Canada 2002:400PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Karkanis SG, Caloia D, Salenieks ME, Kingdom J, Walker M, Meffe F, et al. Randomized controlled trial of rectal misoprostol versus oxytocin in third stage management. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada: JOGC 2002;24(2):149‐54. - PubMed
Canada 2007:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Baskett TF, Persad V, Clough H, Young D. Prophylactic use of misoprostol in the third stage of labor [abstract]. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2005;105(4 Suppl):39S.
-
- Baskett TF, Persad VL, Clough HJ, Young DC. Misoprostol versus oxytocin for the reduction of postpartum blood loss. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2007;97(1):2‐5. - PubMed
China 2001:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Ng PS, Chan ASM, Sin WK, Tang LCH, Cheung KB, Yuen PM. A multicentre randomized controlled trial of oral misoprostol and im syntometrine in the management of the third stage of labour. Human Reproduction 2001;16(1):31‐5. - PubMed
-
- Ng PS, Chan ASM, Sin WK, Tang LCH, Cheung KB, Yuen PM. Comparison of oral misoprostol and intramuscular syntometrine in the management of the third stage of labor ‐ a multicenter randomised controlled trial. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology. Book 4; 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA. 2000:29.
China 2003:400PO vs N {published data only}
-
- Fu YX, Ran KQ, Wang M. Prevention of early postpartum hemorrhage by way of oral misoprostol. Journal of Nursing Science 2003;18(12):910‐1.
China 2004a:600SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Lam H, Tang OS, Lee CP, Ho PC. A pilot‐randomized comparison of sublingual misoprostol with syntometrine on the blood loss in third stage of labor. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2004;83:647‐50. - PubMed
China 2004b:400PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Yuen PM, Ng PS, Sahota DS. A double‐blind randomised controlled trial of oral misoprostol in addition to intra‐muscular syntometrine in the management of the third stage of labour. 30th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 2004 July 7‐9; Glasgow, UK. 2004:62.
China 2007:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Ng PS, Lai CY, Sahota DS, Yuen PM. A double‐blind randomized controlled trial of oral misoprostol and intramuscular syntometrine in the management of the third stage of labor. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2007;63(1):55‐60. - PubMed
-
- Ng PS, Yuen PM, Sahota DS. Comparison of oral misoprostol and intravascular syntocinon in the management of the third stage of labour ‐ a double‐blind randomised controlled trial. 30th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 2004 July 7‐9; Glasgow, UK. 2004:69.
Colombia 2002:50SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Penaranda WA, Arrieta OB, Yances BR. Active management of childbirth with sublingual misoprostol: a controlled clinical trial in the Hospital de Maternidad Rafael Calvo [Manejo activo del alumbramiento con misoprostol sublingual: un estudio clinico controlado en al hospital de maternidad rafael calvo de cartagena]. Revista Colombiana de Obstetricia y Ginecologia 2002;53(1):87‐92.
EEV 2010:800SL vs U {published and unpublished data}
-
- Winikoff B. Misoprostol for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. ClinicalTrials.gov (http://clinicaltrials.gov/) (accessed 20 February 2008) 2008.
-
- Winikoff B, Dabash R, Durocher J, Darwish E, Ngoc NTN, Leon W, et al. Treatment of postpartum hemorrhage with sublingual misoprostol versus oxytocin: results from a randomized, non‐inferiority trial among women not exposed to oxytocin during labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S59.
-
- Winikoff B, Dabash R, Durocher J, Darwish E, Nguyen TN, Leon W, et al. Treatment of post‐partum haemorrhage with sublingual misoprostol versus oxytocin in women not exposed to oxytocin during labour: a double‐blind, randomised, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet 2010;375(9710):210‐6. - PubMed
Egypt 2009:800PR vs U {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nasr A, Shahin AY, Elsamman AM, Zakherah MS, Shaaban OM. Rectal misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;105(3):244‐7. - PubMed
Egypt 2012a:CS400PR vs P {published data only}
-
- Elsedeek MS. Impact of preoperative rectal misoprostol on blood loss during and after elective cesarean delivery. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;118(2):149‐52. - PubMed
Egypt 2012b:CS400SL vs P {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tahan MR, Warda OM, Rashad A, Yasseen AM, Ramzy EA, Ahmady MS, et al. Effects of preoperative sublingual misoprostol on uterine tone during isoflurane anesthesia for cesarean section. Revista Brasileira de Anestesiologia 2012;62(5):625‐35. - PubMed
France 2001:600PO vsP vsU {published data only}
-
- Benchimol M, Gondry J, Mention JE, Gagneur O, Boulanger JC. Role of misoprostol in the delivery outcome. [French] [Place du misoprostol dans la direction de la delivrance.]. Journal de Gynecologie, Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction 2001;30(6):576‐83. - PubMed
Gambia 2004:600PO/SL vs P {published data only}
-
- Walraven G, Dampha Y, Bittaye B, Sowe M, Hofmeyr J. Misoprostol in the treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in addition to routine management: a placebo randomised controlled trial. BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2004;111:1014‐7. - PubMed
Gambia 2005:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Walraven G, Blum J, Dampha Y, Sowe M, Morison L, Winikoff B, et al. Misoprostol in the management of the third stage of labour in the home delivery setting in rural Gambia: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2005;112:1277‐83. - PubMed
Ghana 2000:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Walley RL, Wilson JB, Crane JM, Matthews K, Sawyer E, Hutchens D. A double‐blind placebo controlled randomised trial of misoprostol and oxytocin in the management of the third stage of labour. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2000;107(9):1111‐5. - PubMed
Ghana 2006: 800PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Parsons S, Ntumy YM, Walley RL, Wilson JB, Crane JMG, Matthews K, et al. Rectal misoprostol vs intramuscular oxytocin in the routine management of the third stage of labour. 30th British Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 2004 July 7‐9; Glasgow, UK. 2004:18.
-
- Parsons SM, Walley RL, Crane JM, Matthews K, Hutchens D. Rectal misoprostol versus oxytocin in the management of the third stage of labour. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada 2007;29(9):711‐8. - PubMed
Guinea‐B 2005:600SL vs P {published data only}
-
- Nielsen BB, Hoj L, Hvidman LE, Nielsen J, Cardoso P, Aaby P. Reduced post‐partum bleeding after treatment with sublingual misoprostol: a randomized double‐blind clinical study in a developing country ‐ secondary publication [Reduceret post partum‐blodning efter sublingval misoprostol: et randomiseret dobbeltblindt klinisk studie i et udviklingsland ‐ sekundaerpublikation.]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 2006;168(13):1341‐3. - PubMed
India 2004a:400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Vimala N, Mittal S, Kumar S, Dadhwal V, Mehta S. Sublingual misoprostol versus methylergometrine for active management of third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2004;87:1‐5. - PubMed
India 2005:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Garg P, Batra S, Gandhi G. Oral misoprostol versus injectable methylergometrine in management of the third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2005;91(2):160‐1. - PubMed
India 2006a:CS400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Vimala N, Mittal S, Kumar S. Sublingual misoprostol versus oxytocin infusion to reduce blood loss at cesarean section. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;92(2):106‐10. - PubMed
India 2006b:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Zachariah ES, Naidu M, Seshadri L. Oral misoprostol in the third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;92(1):23‐6. - PubMed
India 2006c:600PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Derman RJ, Kodkany BS, Goudar SS, Geller SE, Naik VA, Bellad MB, et al. Oral misoprostol in preventing postpartum haemorrhage in resource‐poor communities: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006;368(9543):1248‐53. - PubMed
-
- Geller SE, Patel A, Niak VA, Goudar SS, Edlavitch SA, Kodkany BS, et al. Conducting international collaborative research in developing nations. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2004;87(3):267‐71. - PubMed
-
- Goudar SS, Chakraborty H, Edlavitch SA, Naik VA, Bellad MB, Patted SS, et al. Variation in the postpartum hemorrhage rate in a clinical trial of oral misoprostol. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2008;21(8):559‐64. - PubMed
-
- Kodkany BS, Derman RJ, Goudar SS, Geller SE, Edlavitch SA, Naik VA, et al. Initiating a novel therapy in preventing postpartum hemorrhage in rural India: a joint collaboration between the United States and India. International Journal of Fertility & Womens Medicine 2004;49(2):91‐6. - PubMed
India 2006d:400PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Nellore V, Mittal S, Dadhwal V. Rectal misoprostol vs. 15‐methyl prostaglandin F2alpha for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;94(1):45‐6. - PubMed
India 2006e:400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Verma P, Aggarwal N, Jain V, Suri V. A double‐blind randomized controlled trial to compare sublingual misoprostol with methylergometrine for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;94(Suppl 2):S137‐8. - PubMed
India 2006f:600PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Gupta B, Jain V, Aggarwal N. Rectal misoprostol versus oxytocin in the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage ‐ a pilot study. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;94(Suppl 2):S139‐40. - PubMed
India 2008:100/200SL vsU {published data only}
-
- Chhabra S, Tickoo C. Low‐dose sublingual misoprostol versus methylergometrine for active management of the third stage of labor. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2008;34(5):820‐3. - PubMed
India 2009:400/600SL vsU {published data only}
-
- Singh G, Radhakrishnan G, Guleria K. Comparison of sublingual misoprostol, intravenous oxytocin, and intravenous methylergometrine in active management of the third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(2):130‐4. - PubMed
India 2009:400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Vaid A, Dadhwal V, Mittal S, Deka D, Misra R, Sharma JB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of prophylactic sublingual misoprostol versus intramuscular methyl‐ergometrine versus intramuscular 15‐methyl PGF2alpha in active management of third stage of labor. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2009;280(6):893‐7. - PubMed
India 2010:CS800PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Chaudhuri P, Banerjee GB, Mandal A. Rectally administered misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin infusion during cesarean delivery to reduce intraoperative and postoperative blood loss. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2010;109(1):25‐9. - PubMed
India 2012:CS400SL vs P {published data only}
India 2012a:400SL vs U {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chaudhuri P, Biswas J, Mandal A. Sublingual misoprostol versus intramuscular oxytocin for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage in low‐risk women. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;116(2):138‐42. - PubMed
India 2012b:400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Bellad M, Ganachari TDM, Mallapur M. Sublingual (SL) powdered misoprostol (400 mcg) vs IM oxytocin (10 IU) for prevention of postpartum blood loss ‐ a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S124‐5.
-
- Bellad MB, Tara D, Ganachari MS, Mallapur MD, Goudar SS, Kodkany BS, et al. Prevention of postpartum haemorrhage with sublingual misoprostol or oxytocin: a double‐blind randomised controlled trial. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2012;119(8):975‐86. - PubMed
Indonesia 2002:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Dasuki D, Emilia O, Harini S. Randomized clinical trial: the effectiveness of oral misoprostol versus oxytocin in prevention of postpartum hemorrhage [abstract]. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2002;28(1):46.
Iran 2009:CS400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Eftekhari N, Doroodian M, Lashkarizadeh R. The effect of sublingual misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin in reducing bleeding after caesarean section. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2009;29(7):633‐6. - PubMed
Jamaica 2009:400PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Harriott J, Christie L, Wynter S, DaCosta V, Fletcher H, Reid M. A randomized comparison of rectal misoprostol with syntometrine on blood loss in the third stage of labour. West Indian Medical Journal 2009;58(3):201‐6. - PubMed
Korea 2007:CS400PR vs P {published data only}
-
- Hong SC, Kim JW, Park HT, Seol HJ, Kim HJ, Kim SH, et al. Additional rectal misoprostol plus intravenous oxytocin versus intravenous oxytocin for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage after cesarean section. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2007;197(6 Suppl 1):S99, Abstract no: 321.
Mexico 2009:CS800IU vs P {published data only}
-
- Quiroga Diaz R, Cantu Mata R, Tello Gutierrez HE, Puente Villalobos M, Montemayor Garza R, Martinez Mendoza A. Intrauterine misoprostol for the prevention of bleeding cesarean. Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico 2009;77(10):469‐74. - PubMed
Mozam 2001:400PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Bugalho A, Daniel A, Foundes A, Cunha M. Misoprostol for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2001;73:1‐6. - PubMed
Nepal 2011:1000PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Shrestha A, Dongol A, Chawla CD, Adhikari RK. Rectal misoprostol versus intramuscular oxytocin for prevention of post partum hemorrhage. Kathmandu University Medical Journal 2011;33(1):8‐12. - PubMed
Nigeria 2003:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Oboro VO, Tabowei TO. A randomised controlled trial of misoprostol versus oxytocin in the active management of the third stage of labour. Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2003;23(1):13‐6. - PubMed
Nigeria 2007:400PO vs U {published and unpublished data}
-
- Enakpene CA, Morhason‐Bello IO, Enakpene EO, Arowojolu AO, Omigbodun AO. Oral misoprostol for the prevention of primary post‐partum hemorrhage during third stage of labor. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2007;33(6):810‐7. - PubMed
Nigeria 2010:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Afolabi EO, Kuti O, Orji EO, Ogunniyi SO. Oral misoprostol versus intramuscular oxytocin in the active management of the third stage of labour. Singapore Medical Journal 2010;51(3):207‐11. - PubMed
Nigeria 2011:400SL vs P {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fawole AO, Sotiloye OS, Hunyinbo KI, Umezulike AC, Okunlola MA, Adekanle DA, et al. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of misoprostol and routine uterotonics for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2011;112(2):107‐11. - PubMed
Nigeria 2011:600PO vs U {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sadiq UG, Kwanashie O, Mairiga G, Gamaniel S, Isa H, Abdu A, et al. A randomised clinical trial comparing the efficacy of oxytocin injection and oral misoprostol tablet in the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage in Maiduguri Nigeria. International Research Journal of Pharmacy 2011;2(8):76‐81.
Nigeria 2011:CS400SL vs U {published data only}
-
- Owonikoko KM, Arowojolu AO, Okunlola MA. Effect of sublingual misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin on reducing blood loss at cesarean section in Nigeria: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2011;37(7):715‐21. - PubMed
Pakistan 2008:600SL vs P {published data only}
Pakistan 2011:600PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Mobeen N, Durocher J, Zuberi NF, Jahan N, Blum J, Wasim S, et al. Administration of misoprostol by trained traditional birth attendants to prevent postpartum haemorrhage in homebirths in Pakistan: a randomised placebo‐controlled trial. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2011;118:353‐61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mobeen N, Durocher J, Zuberi NF, Jahan N, Blum J, Wasim S, et al. Use of misoprostol by trained traditional birth attendants to prevent postpartum haemorrhage during home deliveries in Pakistan: a randomised placebo‐controlled trial. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S92. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mobeen N, Walraven G. Misoprostol for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage in rural Pakistan (ongoing trial). ClinicalTrials.gov (http://clinicaltrials.gov/) (accessed 21 March 2006).
SA 1998a:400PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Bamigboye AA, Merrell DA, Hofmeyr GJ, Mitchell R. Randomized comparison of rectal misoprostol with syntometrine for management of third stage of labor. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1998;77:178‐81. - PubMed
SA 1998b:400PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem VC, Jager M, Gelbart BR. A randomised placebo controlled trial of oral misoprostol in the third stage of labour. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1998;105(9):971‐5. - PubMed
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Jager M, Rose L, Nikodem VC, Lawrie T. Misoprostol for third stage of labour management: a double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial. Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care; 1997; South Africa. 1997:29‐31.
SA 1998c:400PR vs P {published data only}
-
- Bamigboye AA, Hofmeyr GJ, Merrell DA. Rectal misoprostol in the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage: a placebo controlled trial. Proceedings of the 17th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care; 1998; South Africa. 1998:49‐52. - PubMed
-
- Bamigboye AA, Hofmeyr GJ, Merrell DA. Rectal misoprostol in the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage: a placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1998;179(4):1043‐6. - PubMed
SA 1998d:600/400PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem C, Jager M, Drakely A, Gilbart B. Oral misoprostol for labour third stage management: randomised assessment of side effects. Proceedings of the 17th Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care; 1998; South Africa. 1998:53‐4.
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem VC, Jager M, Drakely AJ. Side effects of oral misoprostol in the third stage of labour: a random allocation placebo controlled trial. Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2000;20(Suppl 1):S40‐1.
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem VC, Jager M, Drakely A. Side‐effects of oral misoprostol in the third stage of labour‐‐a randomised placebo‐controlled trial. South African Medical Journal 2001;91(5):432‐5. - PubMed
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem VC, Jager M, Gelbart BR. A randomised placebo controlled trial of oral misoprostol in the third stage of labour. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1998;105(9):971‐5. - PubMed
SA 2001a:600PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem VC, Jager M, Drakely A. Side‐effects of oral misoprostol in the third stage of labour‐‐a randomised placebo‐controlled trial. South African Medical Journal 2001;91(5):432‐5. - PubMed
-
- Maholwana B, Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem C, Ferreira S, Singata M, Mangesi L, et al. Misoprostol for treating postpartum haemorrhage. 21st Conference on Priorities in Perinatal Care in South Africa; 2002 March 5‐8; Eastern Cape, South Africa. 2002.
SA 2001b:800PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Lokugamage AU, Moodley J, Sullivan K, Rodeck CH, Niculescu L, Tigere P. The Durban primary postpartum haemorrhage study. Women's Health ‐ into the new millennium. Proceedings of the 4th International Scientific Meeting of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists; 1999 October 3‐6; Cape Town South Africa. RCOG, 1999:77‐8.
-
- Lokugamage AU, Sullivan KR, Niculescu I, Tigere P, Onyangunga F, Refaey H, et al. A randomized study comparing rectally administered misoprostol versus Syntometrine combined with an oxytocin infusion for the cessation of primary post partum hemorrhage. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2001;80:835‐9. - PubMed
SA 2004:1000PO/SL/PR vs P {published data only}
SANU 2011:400SL vs P {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hofmeyr GJ. Misoprostol for preventing postpartum hemorrhage. ClinicalTrials.gov (http://clinicaltrials.gov/) (accessed 20 February 2008) 2008.
-
- Hofmeyr GJ, Fawole B, Mugerwa K, Godi NP, Blignaut Q, Mangesi L, et al. Administration of 400mug of misoprostol to augment routine active management of the third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2011;112(2):98‐102. - PubMed
SATAEV 2010:600SL vs P {published data only}
-
- Villar J. Misoprostol to treat postpartum hemorrhage (PPH): a randomized controlled trial (Argentina, Egypt, South Africa, Thailand and Viet Nam). Current Controlled Trials (www.controlled‐trials.com/mrct) (accessed 21 March 2006) 2006.
-
- Widmer M, Blum J, Hofmeyr GJ, Carroli G, Abdel‐Aleem H, Lumbiganon P, et al. Misoprostol as an adjunct to standard uterotonics for treatment of post‐partum haemorrhage: a multicentre, double‐blind randomised trial. Lancet 2010;375(9728):1808‐13. - PubMed
Spain 2009:400SL200PRvsN {published data only}
-
- Carbonell i Esteve JL, Hernandez JMR, Piloto M, Setien SA, Texido CS, Tomasi G, et al. Active management of the third phase of labour plus 400 mug of sublingual misoprostol and 200 mug of rectal misoprostol versus active management only in the prevention of post‐partum haemorrhage. A randomised clinical trial [Manejo activo de la tercera fase del parto mas 400 mug de misoprostol sublingual y 200 mug de misoprostol rectal frente a manejo activo solo en la prevencion de la hemorragia posparto. Ensayo clinico aleatorizado]. Progresos de Obstetricia y Ginecologia 2009;52(10):543‐51.
Switzer 1999:600PO vs P {published data only}
-
- Surbek DV, Fehr PM, Hoesli I, Holzgreve W. Misoprostol for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage: a randomized controlled trial [abstract]. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology; 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA 2000;Book 1:33.
-
- Surbek DV, Fehr PM, Hoesli I, Holzgreve W. Oral misoprostol vs placebo for third stage of labour [Orales misoprostol reduziert den postpartalen blutverlust]. Gynakologisch Geburtshilfliche Rundschau 1999;39:144.
-
- Surbek DV, Fehr PM, Hosli I, Holzgreve W. Oral misoprostol for third stage of labor: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1999;94(2):255‐8. - PubMed
Switzer 2006:CS800PO vsU {published data only}
-
- Lapaire O, Schneider MC, Stotz M, Surbek DV, Holzgreve W, Hoesli IM. Oral misoprostol vs. intravenous oxytocin in reducing blood loss after emergency cesarean delivery. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;95(1):2‐7. - PubMed
Tibet 2009:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Tudor C, Miller S, Nyima, Sonam, Droyoung, Varner M. Preliminary progress report: randomized double‐blind trial of Zhi Byed 11, a Tibetan traditional medicine, versus misoprostol to prevent postpartum hemorrhage in Lhasa, Tibet. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;94(Suppl 2):S145‐6. - PubMed
-
- Wright L. Preventing postpartum hemorrhage using a Tibetan traditional medicine (ongoing trial). ClinicalTrials.gov (http://clinicaltrials.gov/) (accessed 21 March 2006).
Tunis 2009:CS200SL vs P {published data only}
-
- Fekih M, Jnifene A, Fathallah K, Ben Regaya L, Memmi A, Bouguizene S, et al. Benefit of misoprostol for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage in cesarean section: a randomized controlled trial. Journal de Gynecologie, Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction 2009;38(7):588‐93. - PubMed
Turkey 2002:400PR vs P/U {published data only}
-
- Caliskan E, Meydanli M, Dilbaz B, Aykan B, Sonmezer M, Haberal A. Is rectal misoprostol really effective in the treatment of third stage of labor? A randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2002;187:1038‐45. - PubMed
Turkey 2003:400PO vs P/U {published data only}
-
- Caliskan E, Dilbaz B, Meydanli MM, Ozturk N, Narin MA, Haberal A. Oral misoprostol for the third stage of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2003;101(5 Pt 1):921‐8. - PubMed
Turkey 2005:400V/R vs P {published data only}
-
- Ozkaya O, Sezik M, Kaya H, Desdicioglu R, Dittrich R. Placebo‐controlled randomized comparison of vaginal with rectal misoprostol in the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Research 2005;31(5):389‐93. - PubMed
UK 2000:500PO vs U {published data only}
-
- El‐Refaey H, Nooh R, O'Brien P, Abdalla M, Geary M, Walder J, et al. The misoprostol third stage of labour study: a randomised controlled comparison between orally administered misoprostol and standard management. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2000;107(9):1104‐10. - PubMed
UK 2001:CS400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Acharya G, Al‐Sammarai MT, Patel N, Al‐Habib A, Kiserud T. A randomized, controlled trial comparing effect of oral misoprostol and intravenous syntocinon on intra‐operative blood loss during cesarean section. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2001;80(3):245‐50. - PubMed
UK 2001:CS500PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Lokugamage AU, Paine M, Bassaw‐Balroop K, Sullivan KR, El‐Refaey H, Rodeck CH. Active management of the third stage at caesarean section: a randomised controlled trial of misoprostol versus syntocinon. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2001;41(4):411‐4. - PubMed
USA 2001:400PR vs U {published data only}
-
- Gerstenfeld TS, Wing DA. Rectal misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage after vaginal delivery. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2001;185:878‐82. - PubMed
USA 2004:200B vs P {published data only}
-
- Bhullar A, Carlan SJ, Hamm J, Lamberty N, White L, Richichi K. Buccal misoprostol to decrease blood loss after vaginal delivery: a randomized trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2004;104(6):1282‐8. - PubMed
USA 2005:CS200B vs P {published data only}
-
- Hamm J, Russell Z, Botha T, Carlan SJ, Richichi K. Buccal misoprostol to prevent hemorrhage at cesarean delivery: a randomized study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2005;192:1404‐6. - PubMed
WHO 1999:400/600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Lumbiganon P, Hofmeyr J, Gulmezoglu AM, Pinol A, Villar J. Misoprostol dose‐related shivering and pyrexia in the third stage of labour Who collaborative trial of misoprostol in the management of the third stage of labour. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1999;106(4):304‐8. - PubMed
WHO 2001:600PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Gulmezoglu AM, Villar J, Ngoc NTN, Piaggio G, Carroli G, Adetoro L, et al. WHO multicentre randomised trial of misoprostol in the management of the third stage of labour. Lancet 2001;358:689‐95. - PubMed
-
- Lumbiganon P, Villar J, Piaggio G, Gulmezoglu AM, Adetoro L, Carroli G. Side effects of oral misoprostol during the first 24 hours after administration in the third stage of labour. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2002;109:1222‐6. - PubMed
Zim 2001:400PO vs U {published data only}
-
- Kundodyiwa TW, Majoko F, Rusakaniko S. Misoprostol versus oxytocin in the third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2001;75:235‐41. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Al‐Harazi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Harazi AH, Frass KA. Sublingual misoprostol for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. Saudi Medical Journal 2009;30(7):912‐6. - PubMed
Chandhiok 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chandhiok N, Dhillon BS, Datey S, Mathur A, Saxena NC. Oral misoprostol for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage by paramedical workers in India. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;92(2):170‐5. - PubMed
Chandra 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chandra S, Persad V, Young D, Baskett T. A preliminary study of cutaneous blood flow associated with postpartum use of oral misoprostol. Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Canada: JOGC 2004;26(12):1073‐6. - PubMed
Daly 1999 {published data only}
-
- Daly S, Andolina K, Tolosa JE, Roberts N, Wapner R. A randomized controlled trial of misoprostol versus oxytocin in preventing postpartum blood loss. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1999;180(1 Pt 2):S68.
Diab 1999 {published data only}
-
- Diab KM, Ramy AR, Yehia MA. The use of rectal misoprostol as active pharmacological management of the third stage of labor. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 1999;25(5):327‐32. - PubMed
Dickinson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dickinson JE, Doherty DA. Optimization of third‐stage management after second‐trimester medical pregnancy termination. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 2009;201(3):303.e1‐7. - PubMed
Elati 2011 {published data only}
-
- Elati A, Elmahaishi MS, Elmahaishi MO, Elsraiti OA, Weeks AD. The effect of misoprostol on postpartum contractions: a randomised comparison of three sublingual doses. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2011;118(4):466‐73. - PubMed
Jiang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jiang Q, Wang P, Cao W. Effect on different doses of misoprostol to prevent postpartum hemorrhage. Chinese Nursing Research 2001;15(6):313‐4.
Jin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jin LJ, Zhou L. Application of anus misoprostol to decrease the volume of post partum hemorrhage. Journal of Practical Nursing 2000;16(2):9‐10.
Jirakulsawas 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jirakulsawas J, Khooarmompattana S. Comparison of oral misoprostol and intramuscular methylergonovine for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2000;12(4):332.
Khan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Khan RU, El‐Refaey H. Pharmacokinetics and adverse‐effect profile of rectally administered misoprostol in the third stage of labor. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2003;101(5 Pt 1):968‐74. - PubMed
Khanun 2011 {published data only}
-
- Khanun A, Khanum S. Oral versus rectal misoprostol in the prevention of primary postpartum hemorrage. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences 2011;5(3):587‐8.
Kumar 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kumar S. A study to determine the efficacy of 600 mcg misoprostol in prevention of post partum haemorrhage. 54th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 2011 January 5‐9; Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India. 2011:305.
Kushtagi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kushtagi P, Verghese LM. Evaluation of two uterotonic medications for the management of the third stage of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2006;94(1):47‐8. - PubMed
Leader 2002 {published data only}
-
- Leader J, Bujnovsky M, Carlan SJ, Triana T, Richichi K. Effect of oral misoprostol after second‐trimester delivery: a randomized, blinded study. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;100(4):689‐94. - PubMed
Li 2002 {published data only}
-
- Li X, Wang H, Wang J, Cao X L, Ma Y. Prophylactic and therapeutic effect of misoprofil plus oxytocin on postpartum hemorrhage in patients with pregnancy‐induced hypertension syndrome. Journal of Postgraduates of Medicine 2002;25(7):34‐5.
Li 2003 {published data only}
-
- Li DP, Bei HZ. Clinical study on reduction of postpartum bleeding in the risk factors by misoprostol. Hainan Medical Journal 2003;14(11):11‐2.
Lokugamage 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lokugamage AU, Paine M, Bassau‐Balroop H, El‐Refaey K, Sullivan K, Rodek C. Active management of the third stage at caesarean section: misoprostol vs syntocinon. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology (Book 2); 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA. 2000:54.
Mansouri 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mansouri HA, Alsahly N. Rectal versus oral misoprostol for active management of third stage of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2011;283(5):935‐9. - PubMed
Parsons 2006 {published data only}
-
- Parsons SM, Walley RL, Crane JM, Matthews K, Hutchens D. Oral misoprostol versus oxytocin in the management of the third stage of labour. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada 2006;28(1):20‐6. - PubMed
Prata 2005 {published data only}
-
- Prata N, Mbaruku G, Campbell M, Potts M, Vahidnia F. Controlling postpartum hemorrhage after homebirths in Tanzania. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2005;90:51‐5. - PubMed
Rajbhandari 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rajbhandari S, Hodgins S, Sanghvi H, McPherson R, Pradhan YV, Baqui AH. Expanding uterotonic protection following childbirth through community‐based distribution of misoprostol: Operations research study in Nepal. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2010;108(3):282‐8. - PubMed
Ray 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chatterjee A. Misoprostol and the 3rd stage. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology (Book 4); 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA. 2000:29.
-
- Ray A, Mukherjee P, Basu G, Chatterjee A. Misoprostol and third stage of labour. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India 2001;51(6):53‐4.
Rogers 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rogers MS, Yuen PM, Wong S. Avoiding manual removal of placenta: evaluation of intra‐umbilical injection of uterotonics using the pipingas technique for management of adherent placenta. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2007;86(1):48‐54. - PubMed
Sanghvi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sanghvi H, Ansari N, Prata NJV, Gibson H, Ehsan A, Smith JM. Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage at home birth in Afghanistan. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2010;108:276‐81. - PubMed
Shrivasatava 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shrivasatava DD, Khamsara D. Critical evaluation of sublingual misoprostol and methyl ergometrine in active management of third stage of labour. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(Suppl 3):S484.
Soltan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Soltan MH, Faragallah MF, Mosabah MH, Al‐Adawy AR. External aortic compression device: the first aid for postpartum hemorrhage control. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2009;35(3):453‐8. - PubMed
Tripti 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tripti N, Balram S. 400 ug oral misoprostol versus 0.2mg intravenous methyl ergometrine for the active management of third stage of labor. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India 2009;59(3):228‐34.
van Beekhuizen 2009 {published data only}
Van Stralen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Stralen G. Misoprostol in the management of retained placenta ‐ a safe alternative for manual removal? A randomised controlled trial. Current Controlled Trials (www.controlled‐trials.com/) (accessed 30 October 2007).
-
- Stralen G, Veenhof M, Holleboom C, Roosmalen J. No reduction of manual removal after misoprostol for retained placenta: a double‐blind, randomized trial. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2013;92(4):398‐403. - PubMed
Vogel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Vogel D, Burkhardt T, Rentsch K, Schweer H, Watzer B, Zimmerman R, et al. Misoprostol versus methylergometrine: pharmacokinetics in human milk. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2004;191:2168‐73. - PubMed
Xu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Xu H. Misoprostol on preventing postpartum bleeding in cesarean. Hebei Medicine 2003;9(9):806‐7.
Yan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Yan WG, Ling MX, Mao HY. Clinical study on reduction of postpartum bleeding in cesarean operation by misoprostol. Journal of Zhenjiang Medical College 2000;10(3):440‐1.
Zhao 1998 {published data only}
-
- Zhao Y, Li X, Peng Y. Clinical study on reduction of postpartum bleeding in cesarean section by misoprostol. Chung‐Hua Fu Chan Ko Tsa Chih [Chinese Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology] 1998;33:403‐5. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Adanikin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Adanikin AI, Orji EO, Adanikin PO, Olaniyan O. Comparative study of rectal misoprostol to oxytocin infusion in preventing postpartum haemorrhage post‐caesarean section. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(Suppl 3):S825.
-
- Adanikin AI, Orji EO, Fasubaa OB, Onwudiegwu U, Ijarotimi OA, Olaniyan O. The effect of post‐cesarean rectal misoprostol on intestinal motility. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(2):159‐62. - PubMed
-
- Orji EO, Adanikin AI. Prospective randomised double blind study on the effect of post‐caesarean rectal misoprostol on intestinal motility. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(Suppl 3):S446‐S447. - PubMed
Beigi 2009 (Farsi) {published data only}
-
- Beigi A, Tabarestani H, Moini A, Zarrinkoub F, Kazempour M, Hadian Amree A. [Sublingual misoprostol versus intravenous oxytocin in the management of postpartum hemorrhage]. Tehran University Medical Journal 2009;67(8):556‐61.
Fawzy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fawzy AEMA, Swelem M, Abdelrehim AI, Titeli S, Elghazal ZS, El‐Gahwagi MM, et al. Active management of third stage of labor by intravenous ergometrine and rectal versus sublingual misoprostol (a double‐center study). Alexandria Journal of Medicine 2012;48(4):381‐5.
Is 2012 {published data only}
-
- Is S, Gr V, Keranahalli S. Comparison of intramuscular ergometrine and per rectal misoprostol for prophylaxis against atonic post patrum haemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(Suppl 3):S797‐8.
References to ongoing studies
Diop 2011 {published data only}
-
- Diop AR, Frye LJ, Kone Y. Comparing misoprostol and oxytocin in unijectTM for postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) prevention in Mali. ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed April 2013).
Kalahroudi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kalahroudi MA. Comparison of the effect of rectal misoprostol and syntometrin in prevention of post partum hemorrhage. IRCT Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (www.irct.ir) (accessed 6 December 2010).
Moradi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Moradi S. Comparison of misoprostol and oxytocin in reduction of postpartum hemorrhage. IRCT Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (www.irct.ir) (accessed 6 December 2010).
Additional references
AbouZahar 2003
-
- AbouZahar C, Wardlaw T. Maternal mortality in 2000: estimates developed by WHO, UNICEF and UNFPA. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2003.
ACOG 2006
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin: Clinical Management Guidelines for Obstetrician‐Gynecologists Number 76, October 2006: postpartum hemorrhage. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2006;108:1039‐47. - PubMed
Brecht 1987
-
- Brecht T. Effects of misoprostol on human circulation. Prostaglandins 1987;33:S51‐S60. - PubMed
Chong 1997
-
- Chong YS, Chua S, Arulkumaran S. Severe hyperthermia following oral misoprostol in the immediate postpartum period. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1997;90:703‐4. - PubMed
Echt 1991
-
- Echt D, Liebson PR, Mitchell LB, Peters RW, Obias‐Manno D, Barker AH, et al. Mortality and morbidity in patients receiving encainide, flecainide, or placebo. The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial. New England Journal of Medicine 1991;324(12):781‐8. - PubMed
Elati 2012
-
- Elati A, Weeks A. Risk of fever after misoprostol for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage: a meta‐analysis. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2012;120(5):1140‐8. - PubMed
FIGO 2012a
-
- International Federation Of Gynecology Obstetrics. Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage with misoprostol. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(3):213‐4. - PubMed
FIGO 2012b
-
- International Federation Of Gynecology And Obstetrics. Treatment of postpartum hemorrhage with misoprostol. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;119(3):215‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hofmeyr 1998
-
- Hofmeyr GJ. Misoprostol in obstetrics and gynaecology‐‐unregistered, dangerous and essential. South African Medical Journal 1998;88:535‐6. - PubMed
Hundley 2013
-
- Hundley VA, Avan BI, Sullivan CJ, Graham WJ. Should oral misoprostol be used to prevent postpartum haemorrhage in home‐birth settings in low‐resource countries? A systematic review of the evidence. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2013;120(3):277‐85. - PubMed
Leduc 2009
-
- Leduc D, Senikas V, Lalonde AB, Ballerman C, Biringer A, Delaney M, et al. Active management of the third stage of labour: prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada: JOGC 2009;31(10):980‐93. - PubMed
Lumbiganon 1999
-
- Lumbiganon P, Hofmeyr J, Gulmezoglu AM, Villar J. Misoprostol dose‐related shivering and pyrexia in the third stage of labour. WHO Collaborative Trial in the Management of the Third Stage of Labour. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1999;106:304‐8. - PubMed
Mousa 2007
Norman 1991
-
- Norman JE, Thong KJ, Baird DT. Uterine contractility and induction of abortion in early pregnancy by misoprostol and mifepristone. Lancet 1991;338:1233‐6. - PubMed
Qian 1994
RCOG 2009
-
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. RCOG Green‐top Guideline No. 52. RCOG: 2009.
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Smith 2013
Sutherland 2010
-
- Sutherland T, Meyer C, Bishai DM, Geller S, Miller S. Community‐based distribution of misoprostol for treatment or prevention of postpartum hemorrhage: cost‐effectiveness, mortality, and morbidity reduction analysis. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 2010;108(3):289‐94. - PubMed
Tang 2013
-
- Tang J, Kapp N, Dragoman M, Souza JP. WHO recommendations for misoprostol use for obstetric and gynecologic indications. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2013 Feb 19. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

