Once versus twice daily low molecular weight heparin for the initial treatment of venous thromboembolism
- PMID: 23857562
- PMCID: PMC10964127
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003074.pub3
Once versus twice daily low molecular weight heparin for the initial treatment of venous thromboembolism
Abstract
Background: In the initial treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is administered once or twice daily. A once daily treatment regimen is more convenient for the patient and may optimise home treatment. However, it is not clear whether a once daily treatment regimen is as safe and effective as a twice daily treatment regimen. This is the second update of a review first published in 2003.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and safety of once daily versus twice daily administration of LMWH.
Search methods: For this update the Cochrane Peripheral Vascular Diseases Group Trials Search Co-ordinator searched the Specialised Register (last searched May 2013) and CENTRAL (2013, Issue 4).
Selection criteria: Randomised clinical trials in which LMWH given once daily is compared with LMWH given twice daily for the initial treatment of VTE.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors assessed trials for inclusion and extracted data independently.
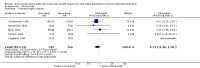
Main results: Five studies were included with a total of 1508 participants. The pooled data showed no statistically significant difference in recurrent VTE between the two treatment regimens (OR 0.82, 0.49 to 1.39; P = 0.47). A comparison of major haemorrhagic events (OR 0.77, 0.40 to 1.45; P = 0.41), improvement of thrombus size (OR 1.41, 0.66 to 3.01; P = 0.38) and mortality (OR 1.14, 0.62 to 2.08; P = 0.68) also showed no statistically significant differences between the two treatment regimens. None of the five included studies reported data on post-thrombotic syndrome.
Authors' conclusions: Once daily treatment with LMWH is as effective and safe as twice daily treatment with LMWH.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
Update of
-
Once versus twice daily LMWH for the initial treatment of venous thromboembolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003074. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003074.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 16;(7):CD003074. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003074.pub3. PMID: 16034885 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Charbonnier 1998 {published data only}
-
- Charbonnier BA, Fiessinger JN, Banga JD, Wenzel E, d'Azemar P, Sagnard L. Comparison of a once daily with a twice daily subcutaneous low molecular weight heparin regimen in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. FRAXODI group. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1998;79(5):897‐901. - PubMed
Holmström 1992 {published data only}
-
- Holmström M, Berglund MC, Granqvist S, Bratt G, Törnebohm E, Lockner D. Fragmin once or twice daily subcutaneously in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis of the leg. Thrombosis Research 1992;67(1):49‐55. - PubMed
-
- Holmström M, Trönebohm E, Berglund MC, Granqvist S, Lockner D. Fragmin (KABI) subcutaneously once or twice daily in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Journal of Internal Medicine Supplement 1990;733:31.
Merli 2001 {published data only}
-
- Merli G, Spiro TE, Olsson CG, Abildgaard U, Davidson BL, Eldor A, et al. Subcutaneous enoxaparin once or twice daily compared with intravenous unfractionated heparin for treatment of venous thromboembolic disease. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;134(3):191‐202. - PubMed
Partsch 1996 {published data only}
-
- Partsch H, Kechavarz B, Mostbeck A, Köhn H, Lipp C. Frequency of pulmonary embolism in patients who have iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis and are treated with once‐ or twice‐daily low‐molecular‐weight heparin. Journal of Vascular Surgery 1996;24(5):774‐82. - PubMed
Siegbahn 1989 {published data only}
-
- Siegbahn A, Y‐Hassan S, Boberg J, Bylund H, Neerstrand HS, Østergaard P, et al. Subcutaneous treatment of deep venous thrombosis with low molecular weight heparin. A dose finding study with LMWH‐Novo. Thrombosis Research 1989;55(6):767‐78. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agnelli 1995 {published data only}
-
- Agnelli G, Iorio A, Renga C, Boschetti E, Nenci GG, Ofosu FA, et al. Prolonged antithrombin activity of low‐molecular‐weight heparins: Clinical implications for the treatment of thromboembolic diseases. Circulation 1995;92(10):2819‐24. - PubMed
Alhenc‐Gelas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Alhenc‐Gelas M, Jestin‐Le Guernic C, Vitoux JF, Kher A, Aiach M, Fiessinger JN. Adjusted versus fixed doses of the low‐molecular‐weight heparin fragmin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Fragmin‐Study Group. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1994;71(6):698‐702. - PubMed
Andersen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Andersen BS. Postoperative activation of the haemostatic system‐‐influence of prolonged thromboprophylaxis in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Haemostasis 1997;27(5):219‐27. - PubMed
Bara 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bara L, Leizorovicz A, Picolet H, Samama M. Correlation between anti‐Xa and occurrence of thrombosis and haemorrhage in post‐surgical patients treated with either Logiparin (LMWH) or unfractionated heparin. Post‐surgery Logiparin Study Group. Thrombosis Research 1992;65(4‐5):641‐50. - PubMed
Beckman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Beckman JA, Dunn K, Sasahara AA, Goldhaber SZ. Enoxaparin monotherapy without oral anticoagulation to treat acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2003;89(6):953‐8. - PubMed
Belcaro 1999 {published data only}
-
- Belcaro G, Nicolaides AN, Cesarone MR, Laurora G, Sanctis MT, Incandela L, et al. Comparison of low‐molecular‐weight heparin, administered primarily at home, with unfractionated heparin, administered in hospital, and subcutaneous heparin, administered at home for deep‐vein thrombosis. Angiology 1999;50(10):781‐7. - PubMed
Bellosta 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bellosta R, Ferrari P, Luzzani L, Carugati C, Cossu L, Talarico M, et al. Home therapy with LMWH in deep vein thrombosis: Randomized study comparing single and double daily administrations. Angiology 2007;58(3):316‐22. - PubMed
Boneu 1998 {published data only}
-
- Boneu B, Navarro C, Cambus JP, Caplain H, d'Azemar P, Necciari J, et al. Pharmacodynamics and tolerance of two nadroparin formulations (10,250 and 20,500 anti Xa IU x ml(‐1)) delivered for 10 days at therapeutic dose. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1998;79(2):338‐41. - PubMed
Bratt 1988 {published data only}
-
- Bratt GA, Törnebohm E, Johanson M, Aberg W, Granqvist S, Lockner D. Clinical experiences in the administration of a low molecular weight heparin (Fragmin, Kabi‐Vitrum) to healthy volunteers and in the treatment of established deep venous thrombosis. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 1988;154(Supplement 543):96‐100. - PubMed
Bratt 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bratt G, Aberg W, Johansson M, Törnebohm E, Granqvist S, Lockner D. Two daily subcutaneous injections of Fragmin as compared with intravenous standard heparin in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1990;64(4):506‐10. - PubMed
Breddin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Breddin HK, Hach‐Wunderle V, Nakov R, Kakkar VV. For the CORTES Investigators. Effects of a low‐molecular‐weight heparin on thrombus regression and recurrent thromboembolism in patients with deep‐vein thrombosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(9):626‐31. - PubMed
Breddin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Breddin HK, Kadziola Z, Scully M, Nakov R, Misselwitz F, Kakkar VV. Risk factors and coagulation parameters in relationship to phlebographic response and clinical outcome in the treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2003;89(2):272‐9. - PubMed
Buller 2004 {published data only}
-
- Buller H, Davidson B, Decousus H, Gallus A, Gent M, Piovella F. Fondaparinux or enoxaparin for the initial treatment of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis. A randomized trial. Revue de Medecine Interne 2005;26(1):82‐3. - PubMed
-
- Buller HR, Davidson BL, Decousus H, Gallus A, Gent M, Piovella F, et al. Fondaparinux or enoxaparin for the initial treatment of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis: a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2004;140(11):867‐73. - PubMed
-
- Buller HR, The Matisse Investigators. Initial outpatient treatment of venous thromboembolism with fondaparinux (Arixtra(R)): The Matisse trials. Blood 2004;104(11):Abstract 705.
-
- The Matisse Investigators. The MATISSE‐DVT trial, a randomized, double‐blind study comparing once‐daily fondaparinux (ATRIXA) with the low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) enoxaparin, twice daily, in the initial treatment of symptomatic deep‐vein thrombosis (DVT). Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2003; Vol. 1, issue Supplement 1:Abstract OC332.
Cosmi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cosmi B, Filippini M, Tonti D, Avruscio G, Ghirarduzzi A, Bucherini E, et al. STEFLUX Investigators. A randomized double‐blind study of low‐molecular‐weight heparin (parnaparin) for superficial vein thrombosis: STEFLUX (Superficial ThromboEmbolism and Fluxum). Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2012;10(6):1026‐35. - PubMed
Erikson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Eriksson BI, Bergqvist D, Kalebo P, Dahl OE, Lindbratt S, Bylock A, et al. Melagatran for thrombin inhibition in orthopaedic surgery. Ximelagatran and melagatran compared with dalteparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip or knee replacement: the METHRO II randomised trial. Lancet 2002;360(9344):1441‐7. - PubMed
Erikson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Eriksson BI, Agnelli G, Cohen AT, Dahl OE, Mouret P, Rosencher N, et al. Direct thrombin inhibitor melagatran followed by oral ximelagatran in comparison with enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip or knee replacement. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2003;89(2):288‐96. - PubMed
Fiessinger 1996 {published data only}
-
- Fiessinger JN, Lopez‐Fernandez M, Gatterer E, Granqvist S, Kher A, Olsson CG, et al. Once‐daily subcutaneous dalteparin, a low molecular weight heparin, for the initial treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1996;76(2):195‐9. - PubMed
Harenberg 1990 {published data only}
-
- Harenberg J, Huck K, Bratsch H, Stehle G, Dempfle CE, Mall K, et al. Therapeutic application of subcutaneous low‐molecular‐weight heparin in acute venous thrombosis. Haemostasis 1990;20(Supplement 1):205‐19. - PubMed
Harenberg 1997 {published data only}
-
- Harenberg J, Stehle G, Blauth M, Huck K, Mall K, Heene DL. Dosage, anticoagulant, and antithrombotic effects of heparin and low‐molecular‐weight heparin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis 1997;23(1):83‐90. - PubMed
Holmström 1997 {published data only}
-
- Holmström M, Lindmarker P, Granqvist S, Johnsson H, Lockner D. A 6‐month venographic follow‐up in 164 patients with acute deep vein thrombosis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1997;78(2):803‐7. - PubMed
Hull 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hull RD, Raskob GE, Brant RF, Pineo GF, Valentine KA. The importance of initial heparin treatment on long‐term clinical outcomes of antithrombotic therapy. The emerging theme of delayed recurrence. Archives of Internal Medicine 1997;157(20):2317‐21. - PubMed
Hull 2000a {published data only}
-
- Hull RD, Pineo GF, Francis C, Bergqvist D, Fellenius C, Soderberg K, et al. For the North American Fragmin Trial Investigators. Low‐molecular‐weight heparin prophylaxis using dalteparin in close proximity to surgery vs warfarin in hip arthroplasty patients: a double‐blind, randomized comparison. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(14):2199‐207. - PubMed
Hull 2000b {published data only}
-
- Hull RD, Raskob GE, Brant RF, Pineo GF, Elliott G, Stein PD, et al. For the American‐Canadian Thrombosis Study Group. Low‐molecular‐weight heparin vs heparin in the treatment of patients with pulmonary embolism. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(2):229‐36. - PubMed
Kakkar 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kakkar VV, Hoppenstead DA, Fareed J, Kadziola Z, Scully M, Nakov R, et al. Randomized trial of different regimens of heparins and in vivo thrombin generation in acute deep vein thrombosis. Blood 2002;99(6):1965‐70. - PubMed
Leizorovicz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Leizorovicz A. IRIS an ongoing, international, multicentre, open, centrally randomised, parallel group study with tinzaparin or unfractionated heparin (ufh) administered subcutaneously (sc) to patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE). XXIst Congress of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6‐12; Geneva 2007:Abstract no: P‐M‐673.
-
- Leizorovicz A. Tinzaparin compared to unfractionated heparin for initial treatment of deep vein thrombosis in very elderly patients with renal insufficiency‐the IRIS Trial. Blood 2008; Vol. 112.
-
- Leizorovicz A. Tinzaparin compared to unfractionated heparin for initial treatment of deep vein thrombosis in very elderly patients with renal insufficiency‐the IRIS Trial [Abstract No. 434]. ASH 2009; Vol. 112, issue 11:166.
-
- Leizorovicz A, Siguret V, Mottier D. Safety profile of tinzaparin versus subcutaneous unfractionated heparin in elderly patients with impaired renal function treated for acute deep vein thrombosis: The Innohep((R)) in Renal Insufficiency Study (IRIS). Thrombosis Research 2011;128(1):27‐34. - PubMed
Leroyer 1998 {published data only}
-
- Leroyer C, Bressollette L, Oger E, Mansourati J, Cheze‐Le Rest C, Nonent M, et al. For the ANTENOX Study Group. Early versus delayed introduction of oral vitamin K antagonists in combination with low‐molecular‐weight heparin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. A randomized clinical trial. Haemostasis 1998;28(2):70‐7. - PubMed
Lindmarker 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lindmarker P, Holmström M, Granqvist S, Johnsson H, Lockner D. Comparison of once‐daily subcutaneous Fragmin(TM) with continuous intravenous unfractionated heparin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1994;72(2):186‐90. - PubMed
Luomanmaki 1996 {published data only}
-
- Luomanmaki K, Grankvist S, Hallert C, Jauro I, Ketola K, Kim HC, et al. A multicentre comparison of once‐daily subcutaneous dalteparin (low molecular weight heparin) and continuous intravenous heparin in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Journal of Internal Medicine 1996;240(2):85‐92. - PubMed
Meyer 1995 {published data only}
-
- Meyer G, Brenot F, Pacouret G, Simonneau G, Gillet Juvin K, Charbonnier B, et al. Subcutaneous low‐molecular‐weight heparin Fragmin versus intravenous unfractionated heparin in the treatment of acute non massive pulmonary embolism: an open randomized pilot study. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1995;74(6):1432‐5. - PubMed
Mismetti 1995 {published data only}
-
- Mismetti P, Reynaud J, Tardy‐Ponce B, Laporte‐Simitsidis S, Scully M, Goodwyn C, et al. Chrono‐pharmacological study of once daily curative dose of a low molecular weight heparin (200 IU antiXa/kg of Dalteparin) in ten healthy volunteers. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1995;74(2):660‐6. - PubMed
Narin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Narin C, Reyhanoglu H, Tulek B, Onoglu R, Ege E, Sarigul A, et al. Comparison of different dose regimens of enoxaparin in deep vein thrombosis therapy in pregnancy. Advances in Therapy 2008;25(6):585‐94. - PubMed
Offord 2004 {published data only}
-
- Offord R, Lloyd AC, Anderson P, Bearne A. Economic evaluation of enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in acutely ill medical patients. Pharmacy World and Science 2004;26(4):214‐20. - PubMed
Petilla 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pettila V, Leinonen P, Markkola A, Hiilesmaa V, Kaaja R. Postpartum bone mineral density in women treated for thromboprophylaxis with unfractionated heparin or LMW heparin. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2002;87(2):182‐6. - PubMed
Pini 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pini M, Aiello S, Manotti C, Pattacini C, Quintavalla R, Poli T, et al. Low molecular weight heparin versus warfarin in the prevention of recurrences after deep vein thrombosis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1994;72(2):191‐7. - PubMed
Sandset 1990 {published data only}
-
- Sandset PM, Dahl T, Stiris M, Rostad B, Scheel B, Abildgaard U. A double‐blind and randomized placebo‐controlled trial of low molecular weight heparin once daily to prevent deep‐vein thrombosis in acute ischemic stroke. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis 1990;16(Supplement):25‐33. - PubMed
Schellong 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schellong SM, Haas S, Greinacher A, Schwanebeck U, Sieder C, Abletshauser C, et al. An open‐label comparison of the efficacy and safety of certoparin versus unfractionated heparin for the prevention of thromboembolic complications in acutely ill medical patients: CERTAIN. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2010;11(18):2953‐61. - PubMed
Simonneau 1993 {published data only}
-
- Simonneau G, Charbonnier B, Decousus H, Planchon B, Ninet J, Sie P, et al. Subcutaneous low‐molecular‐weight heparin compared with continuous intravenous unfractionated heparin in the treatment of proximal deep vein thrombosis. Archives of Internal Medicine 1993;153(13):1541‐6. - PubMed
Simonneau 1997 {published data only}
-
- Simonneau G, Sors H, Charbonnier B, Page Y, Laaban J‐P, Azarian R, et al. For the THESEE Study Group. A comparison of low‐molecular‐weight heparin with unfractionated heparin for acute pulmonary embolism. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(10):663‐9. - PubMed
Stricker 1999 {published data only}
-
- Stricker H, Marchetti O, Haeberli A, Mombelli G. Hemostatic activation under anticoagulant treatment: a comparison of unfractionated heparin vs. nadroparin in the treatment of proximal deep vein thrombosis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1999;82(4):1227‐31. - PubMed
Turpie 2002 {published data only}
-
- Turpie AG, Bauer KA, Eriksson BI, Lassen MR, PENTATHALON 2000 Study Steering Committee. Postoperative fondaparinux versus postoperative enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after elective hip‐replacement surgery: a randomised double‐blind trial. Lancet 2002;359(9319):1721‐6. - PubMed
Wartski 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wartski M, Collignon MA. Incomplete recovery of lung perfusion after 3 months in patients with acute pulmonary embolism treated with antithrombotic agents. THESEE Study Group. Tinzaparin ou Heparin Standard: Evaluation dans l'Embolie Pulmonaire Study. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2000;41(6):1043‐8. - PubMed
Additional references
Anderson 1991
-
- Anderson FA Jr, Wheeler HB, Goldberg RJ, Hosmer DW, Patwardhan NA, Jovanovic B, et al. A population‐based perspective of the hospital incidence and case‐fatality rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The Worcester DVT Study. Archives of Internal Medicine 1991;151(5):933‐8. - PubMed
Bertina 1994
-
- Bertina RM, Koeleman BP, Koster T, Rosendaal FR, Dirven RJ, Ronde H, et al. Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature 1994;369(6475):64‐7. - PubMed
Brandjes 1992
-
- Brandjes DPM, Heijboer H, Büller HR, Rijk M, Jagt H, Cate JW. Acenocoumarol and heparin compared with acenocoumarol alone in the initial treatment of proximal‐vein thrombosis. New England Journal of Medicine 1992;327(21):1485‐9. - PubMed
Büller 1991
-
- Büller HR, Lensing AWA, Hirsch J, Cate JW. Deep vein thrombosis: new non‐invasive diagnostic tests. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1991;66(1):133‐7. - PubMed
Collins 1987
-
- Collins R, Gray R, Godwin J, Peto R. Avoidance of large biases and large random errors in the assessment of moderate treatment effects: the need for systematic overviews. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):245‐54. - PubMed
Dolovich 2000
-
- Dolovich LR, Ginsberg JS, Douketis JD, Holbrook AM, Cheah G. A meta‐analysis comparing low‐molecular‐weight heparins with unfractionated heparin in the treatment of venous thromboembolism: examining some unanswered questions regarding location of treatment, product type, and dosing frequency. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(2):181‐8. - PubMed
Erkens 2010
Gould 1999
-
- Gould MK, Dembitzer AD, Doyle RL, Hastie TJ, Garber AM. Low‐molecular‐weight heparins compared with unfractionated heparin for treatment of acute deep venous thrombosis. A meta‐analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 1999;130(10):800‐9. - PubMed
Heijboer 1990
-
- Heijboer H, Brandjes DPM, Büller HR, Sturk A, Cate JW. Deficiencies of coagulation‐inhibiting and fibrinolytic proteins in outpatients with deep‐vein thrombosis. New England Journal of Medicine 1990;323(22):1512‐6. - PubMed
Heit 2000
-
- Heit JA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O'Fallon WM, Melton LJ 3rd. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population‐based case‐control study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(6):809‐15. - PubMed
Hirsh 1991
-
- Hirsh J. Drug therapy: Heparin. New England Journal of Medicine 1991;324(22):1565‐74. - PubMed
Hirsh 1992
-
- Hirsh J, Levine MN. Low molecular weight heparin. Blood 1992;79(1):1‐17. - PubMed
Holmström 1990
-
- Holmström M, Tornebohm E, Berglund MC, Granqvist S, Lockner D. Fragmin (KABI) subcutaneously once or twice daily in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Journal of Internal Medicine Supplement 1990;733:31.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomised clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. - PubMed
Koopman 1996
-
- Koopman MM, Prandoni P, Piovella F, Ockelford PA, Brandjes DP, Meer J, et al. Treatment of venous thrombosis with intravenous unfractionated heparin administered in the hospital as compared with subcutaneous low‐molecular‐weight heparin administered at home. The Tasman Study Group. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334(11):682‐7. - PubMed
Mantel 1959
-
- Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 1959;22(4):719‐48. - PubMed
Nordstrom 1992
-
- Nordstrom M, Lindblad B, Bergqvist D, Kjellstrom T. A prospective study of the incidence of deep‐vein thrombosis within a defined urban population. Journal of Internal Medicine 1992;232(2):155‐60. - PubMed
Prandoni 1992
-
- Prandoni P, Lensing AWA, Büller HR, Carta M, Cogo A, Vigo M, et al. Comparison of subcutaneous low‐molecular‐weight heparin with intravenous standard heparin in proximal deep‐vein thrombosis. Lancet 1992;339(8791):441‐5. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. Journal of the American Medical Association 1995;273(5):408‐12. - PubMed
van den Belt 1999
-
- Belt AGM, Prins MH, Lensing AW, Castro AA, Clark OA, Atallah AN, et al. Fixed dose subcutaneous low molecular weight heparins versus adjusted dose unfractionated heparin for venous thromboembolism. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1999, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001100] - DOI - PubMed
van der Heijden 2000
-
- Heijden JF, Prins MH, Büller HR. For the initial treatment of venous thromboembolism: are all low‐molecular‐weight heparin compounds the same?. Thrombosis Research 2000;100(2):V121‐30. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Van Dongen 2002
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical