Hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibits mixed lineage kinase 3 to block apoptosis
- PMID: 23857585
- PMCID: PMC3750171
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491985
Hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibits mixed lineage kinase 3 to block apoptosis
Abstract
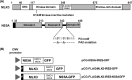
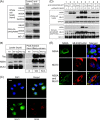
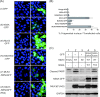
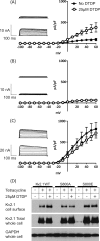
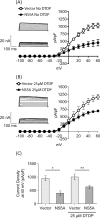
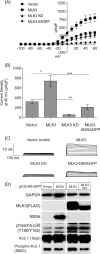
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection results in the activation of numerous stress responses including oxidative stress, with the potential to induce an apoptotic state. Previously we have shown that HCV attenuates the stress-induced, p38MAPK-mediated up-regulation of the K(+) channel Kv2.1, to maintain the survival of infected cells in the face of cellular stress. We demonstrated that this effect was mediated by HCV non-structural 5A (NS5A) protein, which impaired p38MAPK activity through a polyproline motif-dependent interaction, resulting in reduction of phosphorylation activation of Kv2.1. In this study, we investigated the host cell proteins targeted by NS5A to mediate Kv2.1 inhibition. We screened a phage-display library expressing the entire complement of human SH3 domains for novel NS5A-host cell interactions. This analysis identified mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) as a putative NS5A interacting partner. MLK3 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is a member of the MAPK kinase kinase (MAP3K) family and activates p38MAPK. An NS5A-MLK3 interaction was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis. We further demonstrate a novel role of MLK3 in the modulation of Kv2.1 activity, whereby MLK3 overexpression leads to the up-regulation of channel activity. Accordingly, coexpression of NS5A suppressed this stimulation. Additionally we demonstrate that overexpression of MLK3 induced apoptosis, which was also counteracted by NS5A. We conclude that NS5A targets MLK3 with multiple downstream consequences for both apoptosis and K(+) homeostasis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Hepatitis c Virus; Ion Channels; Kv2.1; Mixed Lineage Kinase 3; NS5A; Oxidative Stress; SH3 Domains.
Figures


References
-
- Pawlotsky J. M. (2004) Pathophysiology of hepatitis C virus infection and related liver disease. Trends Microbiol. 12, 96–102 - PubMed
-
- Masaki T., Suzuki R., Murakami K., Aizaki H., Ishii K., Murayama A., Date T., Matsuura Y., Miyamura T., Wakita T., Suzuki T. (2008) Interaction of hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A with core protein is critical for the production of infectious virus particles. J. Virol. 82, 7964–7976 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

