Zinc finger protein 64 promotes Toll-like receptor-triggered proinflammatory and type I interferon production in macrophages by enhancing p65 subunit activation
- PMID: 23857586
- PMCID: PMC3750158
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473397
Zinc finger protein 64 promotes Toll-like receptor-triggered proinflammatory and type I interferon production in macrophages by enhancing p65 subunit activation
Retraction in
-
Withdrawal: Zinc finger protein 64 promotes toll-like receptor-triggered proinflammatory and type I interferon production in macrophages by enhancing p65 subunit activation.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100756. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100756. Epub 2021 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34237908 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Zinc finger Protein 64 promotes Toll-like receptor-triggered proinflammatory and type I interferon production in macrophages by enhancing p65 subunit activation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 26;295(26):8885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.EC120.014572. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32591461 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
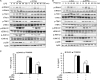
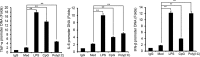
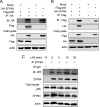
The molecular mechanisms that fine-tune the Toll-like receptor (TLR)-triggered innate immune response need further investigation. As an important transcription factor, zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) play important roles in many cell functions, including development, differentiation, tumorigenesis, and functions of the immune system. However, the role of ZFP members in the innate immune responses remains unclear. Here we showed that the expression of C2H2-type ZFP, ZFP64, was significantly up-regulated in macrophages upon stimulation with TLR ligands, including LPS, CpG oligodeoxynucleotides, or poly(I:C). ZFP64 overexpression promoted TLR-triggered TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-β production in macrophages. Coincidently, knockdown of ZFP64 expression significantly inhibited the production of the above cytokines. However, activation of MAPK and IRF3 was not responsible for the ZFP64-mediated promotion of cytokine production. Interestingly, ZFP64 significantly up-regulated TLR-induced NF-κB activation. ZFP64 could bind to the promoter of the TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-β genes in macrophages only after TLR ligation. Furthermore, ZFP64 associated with the NF-κB p65 subunit upon LPS stimulation, and TLR-ligated macrophages showed a lower level of p65 recruitment to the TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-β gene promoter in the absence of ZFP64. The data identify ZFP64 as a downstream positive regulator of TLR-initiated innate immune responses by associating with the NF-κB p65 subunit, enhancing p65 recruitment to the target gene promoters and increasing p65 activation and, thus, leading to the promotion of TLR-triggered proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production. Our findings add mechanistic insight into the efficient activation of the TLR innate response against invading pathogens.
Keywords: Inflammation; Innate Immunity; Macrophages; NF-κB (NF-κB); Toll-like Receptors (TLR); ZFP64; p65.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Zinc finger protein Gfi1 controls the endotoxin-mediated Toll-like receptor inflammatory response by antagonizing NF-kappaB p65.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;30(16):3929-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00087-10. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20547752 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma negatively regulates IFN-beta production in Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3- and TLR4-stimulated macrophages by preventing interferon regulatory factor 3 binding to the IFN-beta promoter.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 18;286(7):5519-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149823. Epub 2010 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21148557 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of in vitro reprogramming by Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 agonists in murine macrophages: effects of TLR "homotolerance" versus "heterotolerance" on NF-kappa B signaling pathway components.J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):508-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.508. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496438
-
Deciphering the complexity of Toll-like receptor signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Dec;67(24):4109-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0464-x. Epub 2010 Jul 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20680392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pharmacokinetics of Toll-like receptor agonists and the impact on the immune system.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;4(2):275-89. doi: 10.1586/ecp.11.5. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21643519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor resminostat with oncolytic measles vaccine virus as a new option for epi-virotherapeutic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2015 Oct 7;2:15019. doi: 10.1038/mto.2015.19. eCollection 2015. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2015. PMID: 27119111 Free PMC article.
-
A Transcription Factor Addiction in Leukemia Imposed by the MLL Promoter Sequence.Cancer Cell. 2018 Dec 10;34(6):970-981.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Cancer Cell. 2018. PMID: 30503706 Free PMC article.
-
A Squalene-Based Nanoemulsion for Therapeutic Delivery of Resiquimod.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 2;13(12):2060. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122060. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959344 Free PMC article.
-
Six novel susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease and cerebral infarction identified by longitudinal exome-wide association studies in a Japanese population.Biomed Rep. 2018 Aug;9(2):123-134. doi: 10.3892/br.2018.1109. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Biomed Rep. 2018. PMID: 29963304 Free PMC article.
-
Bromodomain protein Brd3 promotes Ifnb1 transcription via enhancing IRF3/p300 complex formation and recruitment to Ifnb1 promoter in macrophages.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 3;7:39986. doi: 10.1038/srep39986. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28045112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takeuchi O., Akira S. (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820 - PubMed
-
- Lee M. S., Kim Y. J. (2007) Signaling pathways downstream of pattern-recognition receptors and their cross talk. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 447–480 - PubMed
-
- Barton G. M., Medzhitov R. (2003) Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 300, 1524–1525 - PubMed
-
- Blasius A. L., Beutler B. (2010) Intracellular toll-like receptors. Immunity 32, 305–315 - PubMed
-
- Netea M. G., Wijmenga C., O'Neill L. A. (2012) Genetic variation in Toll-like receptors and disease susceptibility. Nat. Immunol. 13, 535–542 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

