Targeting SREBP-1-driven lipid metabolism to treat cancer
- PMID: 23859617
- PMCID: PMC4148912
- DOI: 10.2174/13816128113199990486
Targeting SREBP-1-driven lipid metabolism to treat cancer
Abstract
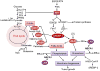
Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of cancer. Oncogenic growth signaling regulates glucose, glutamine and lipid metabolism to meet the bioenergetics and biosynthetic demands of rapidly proliferating tumor cells. Emerging evidence indicates that sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1), a master transcription factor that controls lipid metabolism, is a critical link between oncogenic signaling and tumor metabolism. We recently demonstrated that SREBP-1 is required for the survival of mutant EGFR-containing glioblastoma, and that this pro-survival metabolic pathway is mediated, in part, by SREBP-1-dependent upregulation of the fatty acid synthesis and low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR). These results have identified EGFR/PI3K/Akt/SREBP-1 signaling pathway that promotes growth and survival in glioblastoma, and potentially other cancer types. Here, we summarize recent insights in the understanding of cancer lipid metabolism, and discuss the evidence linking SREBP-1 with PI3K/Akt signaling-controlled glycolysis and with Myc-regulated glutaminolysis to lipid metabolism. We also discuss the development of potential drugs targeting the SREBP-1- driven lipid metabolism as anti-cancer agents.
Figures
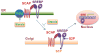
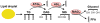
Similar articles
-
An LXR agonist promotes glioblastoma cell death through inhibition of an EGFR/AKT/SREBP-1/LDLR-dependent pathway.Cancer Discov. 2011 Oct;1(5):442-56. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0102. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Cancer Discov. 2011. PMID: 22059152 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SOAT1 Suppresses Glioblastoma Growth via Blocking SREBP-1-Mediated Lipogenesis.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 1;22(21):5337-5348. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2973. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27281560 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin-activated ERBB4 induces the SREBP-2 cholesterol biosynthetic pathway and increases low-density lipoprotein uptake.Sci Signal. 2015 Nov 3;8(401):ra111. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aac5124. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26535009 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018 May 21;38(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0301-4. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29784041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Akt-SREBP nexus: cell signaling meets lipid metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 May;21(5):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20117946 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase Cε Regulates Prostate Cancer Lipid Metabolism and Proliferation by Targeting AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)/Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1 (SREBP-1) Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jul 22;26:e924328. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924328. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32696762 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Alterations in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 and Their Correlation with Lipin.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 12;18(4):1794. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18041794. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33673200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of SREBP and its role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune rheumatic diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 19;15:1398921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1398921. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39224584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR direct crosstalk with STAT5 promotes de novo lipid synthesis and induces hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Aug 14;10(8):619. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1828-2. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31409773 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the SREBP-1/Hsa-Mir-497/SCAP/FASN Oncometabolic Axis Inhibits the Cancer Stem-like and Chemoresistant Phenotype of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 30;23(13):7283. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137283. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Menendez JA, Lupu R. Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nature reviews Cancer. 2007;7:763–77. - PubMed
-
- Medes G, Thomas A, Weinhouse S. Metabolism of neoplastic tissue. IV. A study of lipid synthesis in neoplastic tissue slices in vitro. Cancer research. 1953;13:27–9. - PubMed
-
- Kuhajda FP. Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: new perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition. 2000;16:202–8. - PubMed
-
- Kuhajda FP, Piantadosi S, Pasternack GR. Haptoglobin-related protein (Hpr) epitopes in breast cancer as a predictor of recurrence of the disease. The New England journal of medicine. 1989;321:636–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

