Retention of participants in medication-assisted programs in low- and middle-income countries: an international systematic review
- PMID: 23859638
- PMCID: PMC5312702
- DOI: 10.1111/add.12303
Retention of participants in medication-assisted programs in low- and middle-income countries: an international systematic review
Abstract
Background and aims: Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is a key component in overdose prevention, reducing illicit opiate use and risk of blood-borne virus infection. By retaining participants in MAT programs for longer periods of time, more noticeable and permanent changes in drug use, risk behavior and quality of life can be achieved. Many studies have documented retention in MAT programs in high-income countries, using a 50% average 12-month follow-up retention rate as a marker for a successful MAT program. This study contributes to a systematic understanding of how successful programs have been in retaining participants in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC) over time.
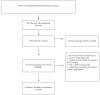
Methods: Using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, we conducted a systematic literature search to identify MAT program studies that documented changes in retention over time for participants in buprenorphine and methadone programs in LMIC. Retention was measured for participants by length of follow-up, type of MAT and treatment dosage.
Results: There were 58 MAT program studies, with 27 047 participants eligible for inclusion in the review. Overall average retention after 12 months was 54.3% [95% confidence interval (CI) = 46.2, 63.7%]. Overall average retention was moderately good for both buprenorphine (48.3%, 95% CI = 22.1, 74.6%) and methadone (56.6%, 95% CI = 45.9%, 67.3%) after 12 months of treatment. Among programs using methadone there was no statistically significant difference in average retention by dosage level, and the 10 highest and lowest dosage programs obtained similar average retention levels after 12 months.
Conclusion: Medication-assisted treatment programs in low- and middle-income countries achieve an average 50% retention rate after 12 months, with wide variation across programs but little difference between those using buprenorphine versus methadone.
Keywords: Buprenorphine; developing countries; low‐ and middle‐income countries; methadone; opiate abuse; opiate substitution programs.
© 2013 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures



Comment in
-
Commentary on Freelemyer et al. (2014): medication-assisted treatment in Africa-need is growing but response remains tepid.Addiction. 2014 Jan;109(1):33-4. doi: 10.1111/add.12364. Addiction. 2014. PMID: 24438111 No abstract available.
References
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) World Drug Report. Vienna: United Nations: 2012.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) Analysis. Vol. 1. Vienna: United Nations: 2006. World Drug Report 2006.
-
- Hall W, Bell J, Carless J. Crime and drug use among applicants for methadone maintenance. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1993;31:123–9. - PubMed
-
- McLellan AT, Arndt IO, Metzger DS, Woody GE, O’Brien CP. The effects of psychosocial services in substance abuse treatment. J Addict Nurs. 1993;5:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Harwood HJ, Napolitano DM, Kristiansen PL, Collins JJ. Economic costs to society of alcohol and drug abuse and mental illness: 1980. Research Triangle Institute; Rockville, MD: 1984.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

