MLK3 promotes metabolic dysfunction induced by saturated fatty acid-enriched diet
- PMID: 23860122
- PMCID: PMC3891220
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00197.2013
MLK3 promotes metabolic dysfunction induced by saturated fatty acid-enriched diet
Abstract
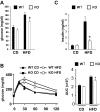
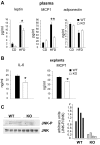
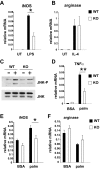
Saturated fatty acids activate the c-Jun NH₂-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, resulting in chronic low-grade inflammation and the development of insulin resistance. Mixed-lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K) that mediates JNK activation in response to saturated fatty acids in vitro; however, the exact mechanism for diet-induced JNK activation in vivo is not known. Here, we have used MLK3-deficient mice to examine the role of MLK3 in a saturated-fat diet model of obesity. MLK3-KO mice fed a high-fat diet enriched in medium-chain saturated fatty acids for 16 wk had decreased body fat compared with wild-type (WT) mice due to increased energy expenditure independently of food consumption and physical activity. Moreover, MLK3 deficiency attenuated palmitate-induced JNK activation and M1 polarization in bone marrow-derived macrophages in vitro, and obesity induced JNK activation, macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in vivo. In addition, loss of MLK3 improved insulin resistance and decreased hepatic steatosis. Together, these data demonstrate that MLK3 promotes saturated fatty acid-induced JNK activation in vivo and diet-induced metabolic dysfunction.
Keywords: inflammation; insulin resistance; mixed-lineage kinase 3; saturated fatty acids.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mixed lineage kinase 3 deficient mice are protected against the high fat high carbohydrate diet-induced steatohepatitis.Liver Int. 2014 Mar;34(3):427-37. doi: 10.1111/liv.12353. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24256559 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the mixed-lineage protein kinase pathway in the metabolic stress response to obesity.Cell Rep. 2013 Aug 29;4(4):681-8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.07.019. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23954791 Free PMC article.
-
Mice lacking NOX2 are hyperphagic and store fat preferentially in the liver.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jun 15;306(12):E1341-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00089.2014. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24760992
-
Cardio-Metabolic Effects of High-Fat Diets and Their Underlying Mechanisms-A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2020 May 21;12(5):1505. doi: 10.3390/nu12051505. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32455838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-Inflammation and Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages in Diabetes and Obesity: The Importance of Metabolites.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 5;12:746151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.746151. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34804028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sab (Sh3bp5) dependence of JNK mediated inhibition of mitochondrial respiration in palmitic acid induced hepatocyte lipotoxicity.J Hepatol. 2015 Jun;62(6):1367-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.01.032. Epub 2015 Feb 7. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25666017 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed-lineage kinase 3 deficiency promotes neointima formation through increased activation of the RhoA pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Jul;34(7):1429-36. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303439. Epub 2014 May 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24790140 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed lineage kinase (MLK) controls tumor development and angiogenesis.Angiogenesis. 2025 May 2;28(3):29. doi: 10.1007/s10456-025-09978-4. Angiogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40314847
-
MLK3 silence suppressed osteogenic differentiation and delayed bone formation via influencing the bone metabolism and disturbing MAPK signaling.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Oct 28;38:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.07.003. eCollection 2023 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 36381243 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of macrophage polarization in adipose tissue.Front Immunol. 2023 May 22;14:1149366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1149366. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37283763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J Biol Chem 275: 9047–9054, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 7: 947–953, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

