Long-term results of adjuvant imatinib mesylate in localized, high-risk, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor: ACOSOG Z9000 (Alliance) intergroup phase 2 trial
- PMID: 23860199
- PMCID: PMC4041735
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a15eb7
Long-term results of adjuvant imatinib mesylate in localized, high-risk, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor: ACOSOG Z9000 (Alliance) intergroup phase 2 trial
Abstract
Objective: To conduct the first adjuvant trial of imatinib mesylate for treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST).
Background: GIST is the most common sarcoma. Although surgical resection has been the mainstay of therapy for localized, primary GIST, postoperative tumor recurrence is common. The KIT protooncogene or, less frequently, platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha is mutated in GIST; the gene products of both are inhibited by imatinib mesylate.
Methods: This was a phase II, intergroup trial led by the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group, registered at ClinicalTrials.gov as NCT00025246. From September 2001 to September 2003, we accrued 106 patients who had undergone complete gross tumor removal but were deemed at high risk for recurrence. Patients were prescribed imatinib 400 mg per day for 1 year and followed with serial radiologic evaluation. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
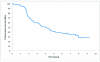
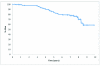
Results: After a median follow-up of 7.7 years, the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 99%, 97%, and 83%, which compared favorably with a historical 5-year OS rate of 35%. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) rates were 96%, 60%, and 40%. On univariable analysis, age and mitotic rate were associated with OS. On multivariable analysis, the RFS rate was lower with increasing tumor size, small bowel site, KIT exon 9 mutation, high mitotic rate, and older age.
Conclusions: Adjuvant imatinib in patients with primary GIST who are at high risk of recurrence prolongs OS compared with that of historical controls. Optimal duration of adjuvant therapy remains undefined. (NCT00025246).
Figures



References
-
- DeMatteo RP, Heinrich MC, El-Rifai WM, et al. Clinical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: before and after STI-571. Hum Pathol. 2002 May;33(5):466–77. - PubMed
-
- Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998 Jan 23;279(5350):577–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

