Establishing optimal quantitative-polymerase chain reaction assays for routine diagnosis and tracking of minimal residual disease in JAK2-V617F-associated myeloproliferative neoplasms: a joint European LeukemiaNet/MPN&MPNr-EuroNet (COST action BM0902) study
- PMID: 23860450
- PMCID: PMC3806250
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2013.219
Establishing optimal quantitative-polymerase chain reaction assays for routine diagnosis and tracking of minimal residual disease in JAK2-V617F-associated myeloproliferative neoplasms: a joint European LeukemiaNet/MPN&MPNr-EuroNet (COST action BM0902) study
Abstract
Reliable detection of JAK2-V617F is critical for accurate diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs); in addition, sensitive mutation-specific assays can be applied to monitor disease response. However, there has been no consistent approach to JAK2-V617F detection, with assays varying markedly in performance, affecting clinical utility. Therefore, we established a network of 12 laboratories from seven countries to systematically evaluate nine different DNA-based quantitative PCR (qPCR) assays, including those in widespread clinical use. Seven quality control rounds involving over 21,500 qPCR reactions were undertaken using centrally distributed cell line dilutions and plasmid controls. The two best-performing assays were tested on normal blood samples (n=100) to evaluate assay specificity, followed by analysis of serial samples from 28 patients transplanted for JAK2-V617F-positive disease. The most sensitive assay, which performed consistently across a range of qPCR platforms, predicted outcome following transplant, with the mutant allele detected a median of 22 weeks (range 6-85 weeks) before relapse. Four of seven patients achieved molecular remission following donor lymphocyte infusion, indicative of a graft vs MPN effect. This study has established a robust, reliable assay for sensitive JAK2-V617F detection, suitable for assessing response in clinical trials, predicting outcome and guiding management of patients undergoing allogeneic transplant.
Figures
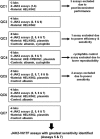
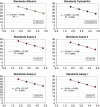
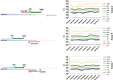
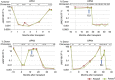
Similar articles
-
JAK2 mutational status and the contribution of TERT and JAK2 polymorphisms to the occurrence of myeloproliferative neoplasms in Eastern Morocco.Afr Health Sci. 2024 Sep;24(3):138-146. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v24i3.18. Afr Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 40777960 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of integrin signaling up-regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines in JAK2-V617F positive hematopoietic cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Aug 11;23(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02358-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40790213 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
Prognostic impact of WT1 expression prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with malignant hematological diseases.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Mar;141(3):523-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1832-y. Epub 2014 Sep 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25238704 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clonogenic assays improve determination of variant allele frequency of driver mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Ann Hematol. 2022 Dec;101(12):2655-2663. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-05000-9. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Ann Hematol. 2022. PMID: 36269400 Free PMC article.
-
The Classification of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Rationale, Historical Background and Future Perspectives with Focus on Unclassifiable Cases.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 12;13(22):5666. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225666. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pegylated interferon alfa-2a in patients with essential thrombocythaemia or polycythaemia vera: a post-hoc, median 83 month follow-up of an open-label, phase 2 trial.Lancet Haematol. 2017 Apr;4(4):e165-e175. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30030-3. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Lancet Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28291640 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mutations and long-term outcome of 217 young patients with essential thrombocythemia or early primary myelofibrosis.Leukemia. 2015 Jun;29(6):1344-9. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.87. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 25801912
-
JAK2 p.V617F detection and allele burden measurement in peripheral blood and bone marrow aspirates in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms.Blood. 2013 Nov 28;122(23):3784-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-515676. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24068492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1779–1790. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:387–397. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365:1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. (eds). WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues IARC: Lyon, France; 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

